This documentation and the Cisco Observability Platform functionalities it describes are subject to change. Data saved on the platform may disappear and APIs may change without notice.
Platform Data
This page provides an overview of the data flow, collection, ingestion, data model, processing, and storage in the Cisco Observability Platform.
Data Flow
The diagram below offers a simplified high-level view of how data is collected, processed, and stored in the platform for a given solution. The following sections delve into each stage of the data flow in more detail.
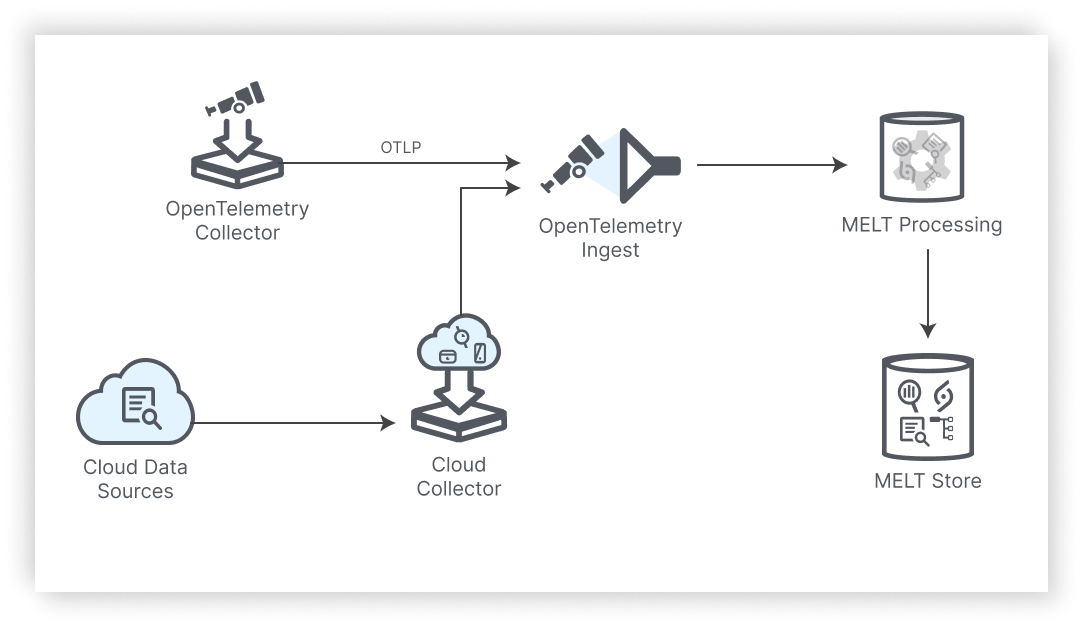
Data Collection
Your solutions on the Cisco Observability Platform collect data through several mechanisms. The Cisco Observability Platform provides Cisco collectors for aggregating Kubernetes®, container, OLTP data, and logs.
| Collector Name | Data Collected |
|---|---|
|
Cisco AppDynamics Distribution of OpenTelemetry Collector |
Receives OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP) data from Infrastructure Collector, Cluster Collector, and Log Collector. Also receives the data from applications instrumented with the OpenTelemetry Operator for Kubernetes tracer SDKs/Agents or any other OTLP sources over gRPC and HTTP and exported to the platform. |
| Cluster Collector | Collects Kubernetes data. |
|
Infrastructure Collector |
Collects the server and container data, known as Host Monitoring. |
|
Log Collector |
Collect the logs. |
OLTP Ingestion
The Cisco Observability Platform provides a Common Ingestion Service to ingest data in one efficient way. The Cisco collectors publish OpenTelemetry metric data to the Common Ingestion Service, but you can also use the Common Ingestion API to push data directly into the pipeline.
Data Model
The Cisco Observability Platform uses the Flexible Metadata Model (FMM) for modeling data for solutions. The data stored in the platform is based on this metadata model and can be added to or modified. FMM differs from a fixed metadata model expected to exist in code logic and requires more effort to adapt to changing monitoring requirements.
To illustrate how you might use FMM in a solution, you could add a new attribute called "Optimization Score" to all Kubernetes entities or create an entity model for an observed Git repository. The entity model could include entity types with associated metrics and events for repositories, branches, and committers. The model for the Kubernetes or Git entity can be updated if you new attributes are needed or removed if some attributes have been deprecated.
MELT Processing
The MELT data is aggregated, processed, and transformed into JSON objects based on the defined Flexible Metadata Model (FMM) for the solution. FMM enables your solution to model your domain and observe measurements on your domain entities for correlation and querying.
MELT and Knowledge Store
The Knowledge Store houses the JSON objects and enables the encapsulated MELT data to be easily correlated and queried with UQL.