How a Session is Maintained
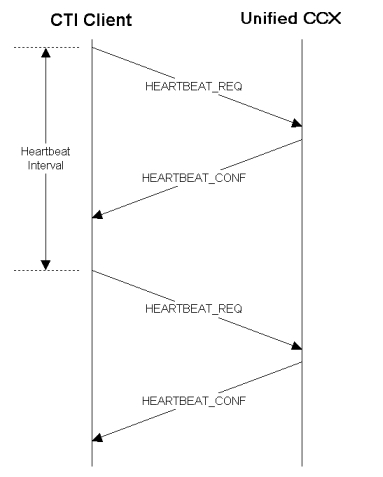
To detect and handle transmission failures, the client must send a HEARTBEAT_REQ message, see HEARTBEAT_REQ, to the server whenever no messages have been sent for the heartbeat interval or sooner. On receipt of a HEARTBEAT_REQ message, the server immediately responds with a HEARTBEAT_CONF message, defined in HEARTBEAT_CONF. If three heartbeats go unconfirmed, the client must declare a session failure and reset the TCP connection.
The heartbeat interval is solely determined by the client and represents a reasonable balance between the speed of failure detection and the network bandwidth consumed by heartbeat messages and their corresponding confirmations. A maximum value of 30 seconds is accepted by the server
The server does not initiate HEARTBEAT_REQ messages. Failure detection on the server is accomplished using the IdleTimeout value from the OPEN_REQ message. When heartbeat messages are implemented, the client must set this value to four times the heartbeat interval. If the server does not receive any messages (including HEARTBEAT_REQ messages) for this period of time, the server declares a session failure and resets the TCP connection.
The server may respond to a HEARTBEAT_REQ message with a FAILURE_CONF message. This indicates to the client that the server is off-line, and the client must reset the TCP connection.
Note | Heartbeat messages must be sent regardless of line activity or in-activity. |
Figure 1 depicts the heartbeat message flow.
Note | You need to synchronize the time of the client and the server and you need to make sure the intervals between the heartbeats are identical. |