Getting Started
This guide demonstrates NB API usage through user scenarios and provides examples to serve as references for integrating external systems with CNC.
This guide shows how to use the CNC NB API to configure VPN (L2/L3) services with SR-TE and RSVP-TE, helping administrators and developers automate workflows to meet SLA requirements.
Prerequisites
Before using the examples in this guide, ensure that:
- Install and configure CNC with the corresponding release version.
- Set up and integrate the required applications and NSO with CNC.
- Ensure devices and network topology match the example scenarios or adjust them accordingly.
- Apply Day-0 configurations for devices before running the examples.
Refer to the CNC Installation and Administration guides for detailed setup instructions.
Network topology for the examples
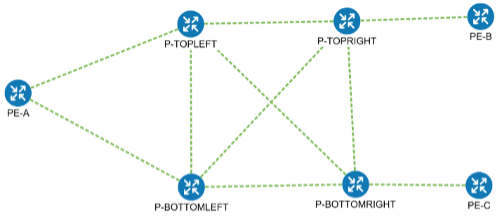
The examples in this guide use three PE devices from the network topologies mentioned above. If the devices and network topology onboarded to the CNC do not match the above topology, adjust the data used in the API calls within the input files accordingly.
| PE Device | Host Name | TE Router Id |
|---|---|---|
| PE-A | PE-A | 100.100.100.5 |
| PE-B | PE-B | 100.100.100.6 |
| PE-C | PE-C | 100.100.100.7 |
Download and setup example scripts
Follow these instructions to set up the scripts for execution on the target CNC setup.
- Download cnc-api-examples.tar.gz and untar in user home directory for the example scripts that are used in this guide.
- Edit the
~/cnc-api-examples/envfile to update the CNC server host, port, and user credentials. - Run the
get-cnc-jwt.shscript to retrieve the JWT token required for authenticating API calls. - Invoke each use case script after optionally updating the input files according to the CNC environment and device/network topology.
Contents of cnc-api-examples.tar.gz
After unzipping cnc-api-examples.tar.gz, you should see
- common-scripts folder that contains environment, common, and authentication script files.
- Multiple use case folders each contain
- Use case example scripts at the root.
- input folder that contains files used as input data to API execution.
- output folder to produce files to store the API execution output data.
- work folder to generate the input files from templates to use as input data to API execution.
/cnc-api-examples
├── common-scripts
│ ├── cnc-api-common.sh
│ ├── env
│ └── get-cnc-jwt.sh
├── [usecase-folder]
│ ├── <usecase-script>.sh
│ ├── input
│ │ ├── <api-input>.json
│ ├── output
│ │ ├── <api-output>.json
│ └── work
│ │ ├── <transformed-api-input>.json
Authentication and Authorization
Accessing the CNC NB API requires Authentication and Authorization. CNC uses JWT-based authentication, obtained through a two-step process. API-level access control and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in CNC manage the authorization of each API.
Obtaining the JWT token
The example script retrieves the JWT token and saves it in a dot file under the user's directory for use in NB API calls.
Invoking the script to get the JWT
cd ~/cnc-api-examples;./common-scripts/get-cnc-jwt.sh
get-cnc-jwt.sh
#!/bin/bash
# This script can be invoked to obtain the JWT token that can be reused in the other usecase scripts while invoking the API.
export PRJ=$(cd `dirname $0`; pwd)
. $PRJ/env
. $PRJ/cnc-api-common.sh
# Get the JWT from CW endpoint and save to a file
get_jwt
# Read from file and export it as AUTH_TOKEN_HDR
export_jwt
echo $AUTH_TOKEN_HDR
API Invocation to obtain the JWT (cnc-api-commons.sh)
# Get authentication token (JWT) from CNC to use it in API authentication
get_jwt() {
# getting JWT to use in CNC API authentication is a two-step process
# Step 1. Get the Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT)
# Step 2. Use the TGT to get the JWT
# Step 1. Invoke this URL with the username and password in the POST payload.
export CNC_API_TGT_URL="https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/crosswork/sso/v1/tickets"
set -x
response=$(curl $CURL_OPTS -X POST $CNC_API_TGT_URL \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
-H 'Accept: text/plain' \
-d "username=${CNC_USER}&password=${CNC_PASSWORD}" \
)
# Step 2: Invoke the JWT URL with the TGT and forwarding service URL in the POST payload.
export CNC_API_JWT_URL="https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/crosswork/sso/v2/tickets/jwt"
response=$(curl $CURL_OPTS -X POST $CNC_API_JWT_URL \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
-d "tgt=$response&service=https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/app-dashboard" \
)
set +x
# Step 3. Only for the purpose of example. Store it in ~/.cnc-jwt file
echo $response > $CNC_JWT_FILE
}
# Read JWT from a file and format the AUTH_TOKEN_HDR to use in API calls
export_jwt() {
# export AUTH_TOKEN_HDR="Authorization: Bearer $response"
export CNC_JWT=$(cat $CNC_JWT_FILE)
export AUTH_TOKEN_HDR="Authorization: Bearer $CNC_JWT"
}
Example Script Environment Variables
The example script defines a set of environment variables necessary to run the use case scripts.
- To learn the CNC Server host, port and user credentials - in ~/cnc-api-examples/evn
- To reuse the API endpoints root contexts - in ~/cnc-api-examples/cnc-api-commons.sh
Env script that contains the target server details
# Main environment script that contains variables of the target CNC server endpoint details for authentication and building root context
# Update the host, port, user, password according to the target CNC. Recommended to add this env to the user environment (e.g., .bash_profile)
x=${CNC_HOST:=127.0.0.1}
x=${CNC_PORT:=30603}
x=${CNC_USER:=admin}
x=${CNC_PASSWORD:=changeit}
x=${CNC_JWT_FILE:=~/.cnc-jwt}
export CNC_HOST
export CNC_PORT
export CNC_USER
export CNC_PASSWORD
export CNC_JWT_FILE
x=${CURL_OPTS:="-k -s"}
export CURL_OPTS
API Endpoint Root Context Environment variables used in the scripts
# Standard CNC NBI URL ROOT CONTEXTS
# Service Provisioning API Endpoint Root Context
export CNC_NSO_RESTCONF_CTX="https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/crosswork/proxy/nso/restconf"
# CAT Service Inventory API Endpoint Root Context
export CNC_CAT_RESTCONF_CTX="https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/crosswork/nbi/cat-inventory/v1/restconf"
# COE Transport Engineering API Endpoint Root Context
export CNC_COE_RESTCONF_CTX="https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/crosswork/nbi/optima/v2/restconf"
# CW Topology API Endpoint Root Context
export CNC_TOPOLOGY_RESTCONF_CTX="https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/crosswork/nbi/topology/v3/restconf"
# standard HTTP headers for RESTCONF
export RESTCONF_CONTENT_TYPE_HDR="Content-Type: application/yang-data+json"
export RESTCONF_ACCEPT_HDR="Accept: application/yang-data+json"
# standard HTTP headers for REST
export REST_CONTENT_TYPE_HDR="Content-Type: application/json"
export REST_ACCEPT_HDR="Accept: application/json"
# Default: Set to RESTCONF headers
export CONTENT_TYPE_HDR="$RESTCONF_CONTENT_TYPE_HDR"
export ACCEPT_HDR="$RESTCONF_ACCEPT_HDR"
# default. change to POST, PUT, PATCH before http_create_update
export HTTP_METHOD="GET"
# HTTP code from an API call is exported.
export HTTP_CODE
Service Yang Models
Intent based service data for service provisioning and retrieval NB APIs used in CNC CAT(Crosswork Active Topology) is based on the yang models defined in Cisco NSO T-SDN Function Pack Bundle. For more details, see Cisco NSO Transport SDN Function Pack Bundle User Guide.
Using NSO Restconf API
CNC defined an NB API (North Bound Application Programming Interface) endpoint to use NSO (Cisco Network Service Orchestrator) RESTCONF interface to provision and retrieve intent based services through CNC NB API. In addition to provisioning and retrieving the intent based service data, this endpoint may be used to access other data or operations supported by NSO using RESTCONF Interface.
CNC NB API Endpoint for NSO Restconf Inteface
https://$CNC_HOST:$CNC_PORT/crosswork/proxy/nso/restconf/...
Example usage of CNC NB API Endpoint for NSO Restconf Inteface
curl -k -X GET 'https://192.168.1.1:30603/crosswork/proxy/nso/restconf/data/ietf-l2vpn-ntw:l2vpn-ntw/vpn-services/vpn-service=l2vpn-123?content=config' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/yang-data+json' \
-H 'Accept: application/yang-data+json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCIsImtpZCI6IjZlNjcxZjEzLWJjODEtNDViNy1iZGZmLTY5MDU5NTU3YzcwMSJ9....'
NSO Documentation References
For Details on NSO supported Retconf API, see NSO Documentation on Restconf API