Authentication and Authorization Guide
Introduction
Cisco Catalyst Center has a REST API that an authenticated and authorized user can leverage to do operations over an HTTPS connection.
After authentication, the user receives a token from the API endpoint and needs to include it in every API request as part of the X-Auth-Token header.
Goal
This guide aims to help you to create a script that authenticates against the Catalyst Center API and obtains the authorization token that is needed to make requests to the API.
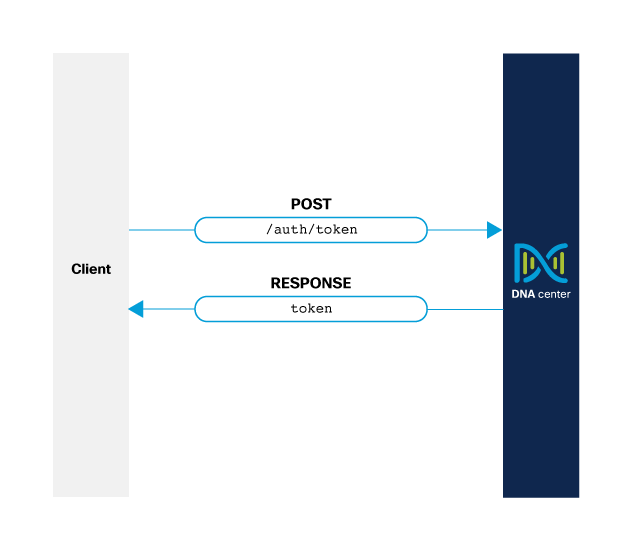
Endpoints and methods used
- POST
/dna/system/api/v1/auth/token
Prerequisites
For this module, it's helpful if you know the basics of Python and REST APIs. If you must catch up, refer these links:
Environment
This guide was developed using:
Authentication API
In this guide, we use the authentication endpoint /dna/system/api/v1/auth/token, which is valid for version 1.2.6 and above. The HTTP method for this endpoint is POST. Users must send their credentials using Basic Authentication.
Note: For systems with versions below, the endpoint is
/api/system/v1/auth/token.
Basic Authentication
Authentication is done by using the Basic authentication scheme, as defined in RFC 7617.
The format of the credentials is USERNAME:PASSWORD and it must be base64 encoded. Then, send the encoded string as part of the Authorization header over clear text. Therefore, it's highly recommended to do this over an HTTPS/TLS connection.
AES Key Encryption
Catalyst Center now supports AES key encryption for token APIs. This optional feature formats the authorization header as a base 64 encoded string of a 256-bits AES key.
The format of the string is CSCO-AES-256 credentials=Base64Encode(AESEncrypt(username:password , aes256 key)).
The AESEncrypt first encrypts the username:password pair with a 256 bits AES key and then Base64Encode encodes the result in base 64 string format.
The AES256 scheme authorizes, as defined in RFC 2617.
Note:
- You can enable the AES key encryption from the Catalyst Center system configuration.
- If you disable the AES key encryption from the Catalyst Center system configuration, the default basic authentication is enabled by default.
Token
After authentication, the user receives a token from the API endpoint and needs to include it in every request as part of the X-Auth-Token header.
Authentication Code
We create a Python script that authenticates and prints the token necessary for authentication.
We use the Python requests library, importing both the requests library but also the HTTPBasicAuth specifically, which simplifies the Basic Authentication process.
import requests
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
Next, we import the urllib3 library and call the disable_warnings() function. This is NOT recommended on a production environment. We use it here in the development environment to avoid the warning that we would get of using a self-signed certificate in Catalyst Center.
import urllib3
urllib3.disable_warnings()
Next, we define four general variables of the script:
- Base URL: IP Address or Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the Catalyst Center server
- Auth URL: API endpoint used for authentication
- Username: Catalyst Center USERNAME
- Password: Catalyst Center PASSWORD
BASE_URL = 'https://10.10.10.181'
AUTH_URL = '/dna/system/api/v1/auth/token'
USERNAME = '<USERNAME>'
PASSWORD = '<PASSWORD>'
Finally, you perform the request using POST, which returns a JSON body with the token. Use the verify=False parameter to query a server with a self-signed certificate. In a production environment with a valid certificate generated by a trusted certificate authority, you don't need it.
response = requests.post(baseUrl + authUrl, auth=HTTPBasicAuth(USERNAME, PASSWORD), verify=False)
print(response.json()['Token'])
Code
The repository for this guide is here. The complete code appears as below:
# Module import
import requests
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
# Disable SSL warnings. Not needed in production environments with valid certificates
import urllib3
urllib3.disable_warnings()
# Authentication
BASE_URL = 'https://<IP Address>'
AUTH_URL = '/dna/system/api/v1/auth/token'
USERNAME = '<USERNAME>'
PASSWORD = '<PASSWORD>'
response = requests.post(BASE_URL + AUTH_URL, auth=HTTPBasicAuth(USERNAME, PASSWORD), verify=False)
print(response.json()['Token'])