Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses detected on assets that can be exploited by a potential attacker to perform malevolent actions on the network.
Vulnerabilities are detected in Cisco Cyber Vision thanks to rules stored in the Knowledge DB. These rules are sourced from several CERTs (Computer Emergency Response Teams), manufacturers and partner manufacturers (such as Schneider or Siemens). Technically, vulnerabilities are generated from the correlation of the Knowledge DB rules and normalized asset and component properties. A vulnerability is detected when an asset or a component matches a Knowledge DB rule.
A vulnerability can be acknowledged to hide it from the active vulnerability list.
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs)
Launched by MITRE in 1999, Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a catalog of publicly disclosed security vulnerabilities. A security vulnerability is a weakness in a computer system that attackers can leverage to violate the security policy of a system. By exploiting a vulnerability, an attacker might access unauthorized resources or threaten the availability of the system.
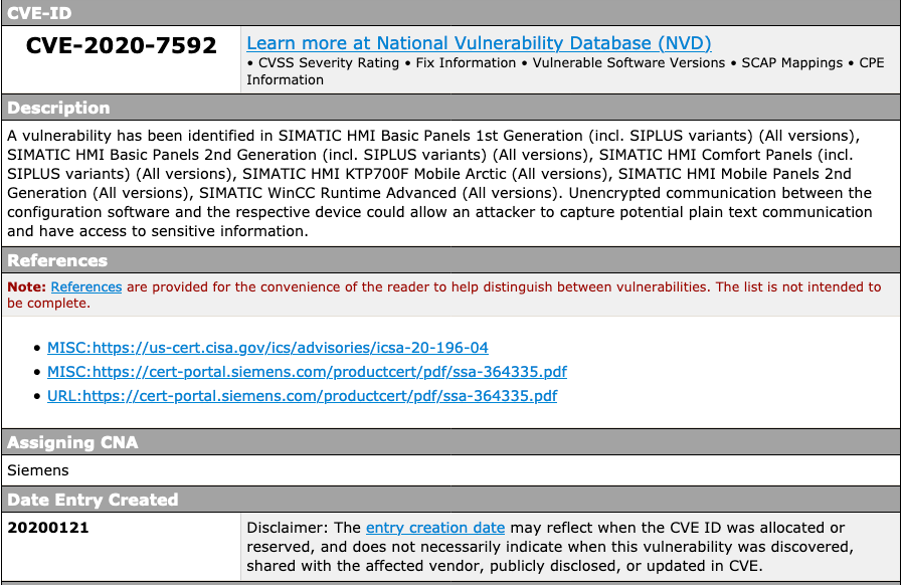
Each vulnerability within the catalog is assigned an identification number (CVE ID), a description, a publication date, a severity score, and at least one public reference that provides technical details and possible remediation. For instance, the CVE entry with ID CVE-2020-7592 references a vulnerability impacting various Siemens devices and components where data integrity can be compromised.
source: cve.mitre.org
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
To measure the severity of a vulnerability, Common Vulnerability and Exposure (CVE) entries are often assigned a CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) score. The CVSS score provides a numerical evaluation, out of 10, of the overall threat raised by the presence of a given vulnerability on a computer system. The base CVSS score is computed by considering aspects such as the complexity of the attack needed to exploit the vulnerability, the attack vector (local or through a network), and the possible impacts of an exploitation on the system. Security teams use CVSS scores as part of their vulnerability management program to prioritize severe vulnerabilities and improve the security posture of computer systems. While CVSS is currently on version 3.1, version 2 is still widely used. Both are supported by Cisco Cyber Vision.
CVSS scores are divided into the following four categories:
- 9-10: Critical vulnerability
- 7-8.9: High severity vulnerability
- 4-6.9: Medium severity vulnerability
- 0.1-3.9: Low severity vulnerability
Cisco Security Risk Score
The Cisco Security Risk Score, which is powered by Cisco Vulnerability Management, is represented on a scale from 0-100 (least risky to most risky). It quantifies the risk of a vulnerability by looking beyond technical severity to understand how real-world attackers are leveraging the vulnerability in the wild—if at all.
The Cisco Security Risk Score uses the following ranges:
| Score Range | Color | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| 0-33 | Green | Low |
| 34-66 | Amber | Medium |
| 67-100 | Red | High |