This documentation corresponds to an older version of the product, is no longer updated, and may contain outdated information.
Please access the latest versions from https://cisco-tailf.gitbook.io/nso-docs and update your bookmarks. OK
The purpose of this section is to get started with NSO, learn the basic operational scenarios and get acquainted with the most common CLI commands.
Make sure that you have installed NSO and that you have sourced the
ncsrc file in
$NCS_DIR. This sets up the paths and
environment variables in order to run NSO. As this must be done
every time before running NSO, it is recommended to add it
in your profile.
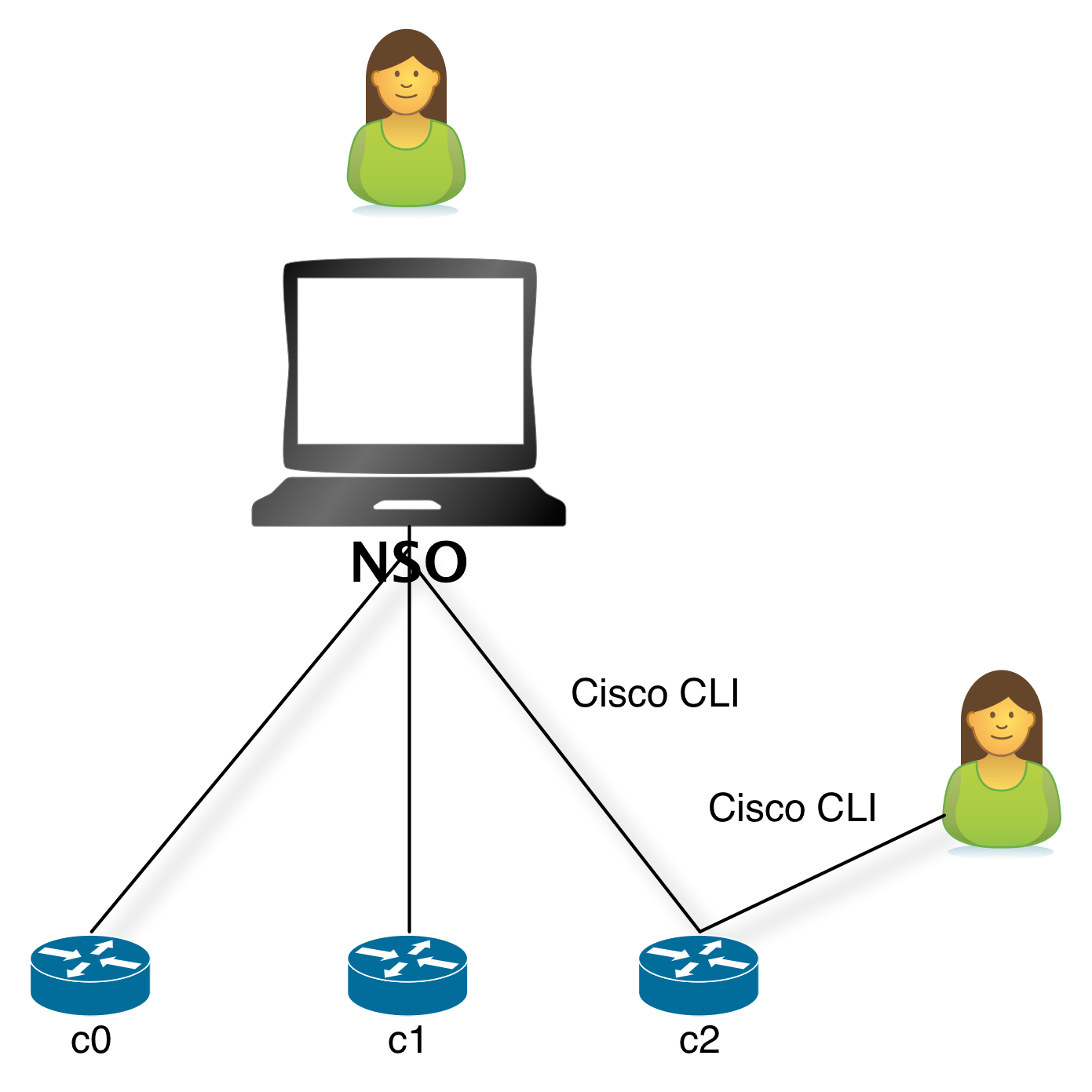
We will use the NSO network simulator to simulate three Cisco IOS routers. NSO will talk Cisco CLI to those devices. You will use the NSO CLI and Web UI to perform the tasks. Sometimes you will use the native Cisco device CLI to inspect configuration or do out of band changes.
Note that both the NSO software (ncs) and the
simulated network devices run on your local machine.
Go to
examples.ncs/getting-started/using-ncs/1-simulated-cisco-ios.
Most of this section follows the procedure in the
README file so it is useful to have that
open as well. First of all we will generate a network
simulator with 3 Cisco devices. They will be called
c0, c1, and c2.
Perform the following command:
$ ncs-netsim create-network $NCS_DIR/packages/neds/cisco-ios 3 cThis creates three simulated devices all running Cisco IOS and the will be named c0, c1, c2. Start the simulator:
$ ncs-netsim start
DEVICE c0 OK STARTED
DEVICE c1 OK STARTED
DEVICE c2 OK STARTEDRun the CLI towards one of the simulated devices
$ncs-netsim cli-i c1admin connected from 127.0.0.1 using console * c1>enablec1#show running-configclass-map m match mpls experimental topmost 1 match packet length max 255 match packet length min 2 match qos-group 1 ! ... c1# exit
This shows that the device has some initial configurations.
The previous step started the simulated Cisco devices. It is
now time to start NSO. The first action is to prepare
directories needed for NSO to run and populate NSO with
information of the simulated devices. This is all done with
the ncs-setup command. Make sure you are
in the
examples.ncs/getting-started/using-ncs/1-simulated-cisco-ios
directory. (Again ignore the details for time being).
$ ncs-setup --netsim-dir ./netsim --dest . Note the "." at the end of the command referring to current directory. What the command does is to create directories needed for NSO in the current directory and populates NSO with devices that are running in netsim. We call this the "run-time" directory.
Start NSO;
$ ncs
Start the NSO CLI as user "admin" with a Cisco XR style CLI:
$ ncs_cli -C -u admin
NSO also supports a J-style CLI, that is started by using a -J modification to the command like this:
$ ncs_cli -J -u adminThroughout this user guide we will show the commands in Cisco XR style.
At this point NSO only knows the address, port, and authentication information of the devices. This management information was loaded to NSO by the setup utility. It also tells NSO how to communicate with the devices by using NETCONF, SNMP, Cisco IOS CLI etc. Although at this point, the actual configuration of the individual devices is un-known.
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device
devices device c0
address 127.0.0.1
port 10022
...
authgroup default
device-type cli ned-id cisco-ios
state admin-state unlocked
config
no ios:service pad
no ios:ip domain-lookup
no ios:ip http secure-server
ios:ip source-route
!
! ...
Let us analyze the above CLI command. First of all, when you start the NSO CLI it starts in operational mode, so in order to show configuration data you have to explicitly say show running-config.
NSO manages a list of devices, each device is reached by the path devices device "name" . You can use standard tab completion in the CLI to learn this.
The address and port fields tells
NSO where to connect to the device. For now they all live in
local host with different ports. The device-type
structure tells NSO it is a CLI device and the specific CLI is
supported by the Network Element Driver (NED)
cisco-ios. A more detailed explanation on how to
configure the device-type structure and how to chose NEDs will
be addressed later in this guide.
So now NSO can try to connect to the devices:
admin@ncs# devices connect
connect-result {
device c0
result true
info (admin) Connected to c0 - 127.0.0.1:10022
}
connect-result {
device c1
result true
info (admin) Connected to c1 - 127.0.0.1:10023
}
connect-result {
device c2
result true
info (admin) Connected to c2 - 127.0.0.1:10024
}....NSO does not need to have the connections "active" continuously, instead NSO will establish a connection when needed and connections are pooled to conserve resources. At this time NSO can read the configurations from the devices and populate the configuration database, CDB.
The following command will synchronize the configurations of the devices with the CDB and respond with "true" if successful:
admin@ncs# devices sync-from
sync-result {
device c0
result true
}....
The NSO data-store, CDB, will store configuration for every
device at the path devices device "name"
config, everything after this path is configuration
in the device. NSO keeps this synchronized. The
synchronization is managed with the following principles:
-
At initialization NSO can discover the configuration as shown above.
-
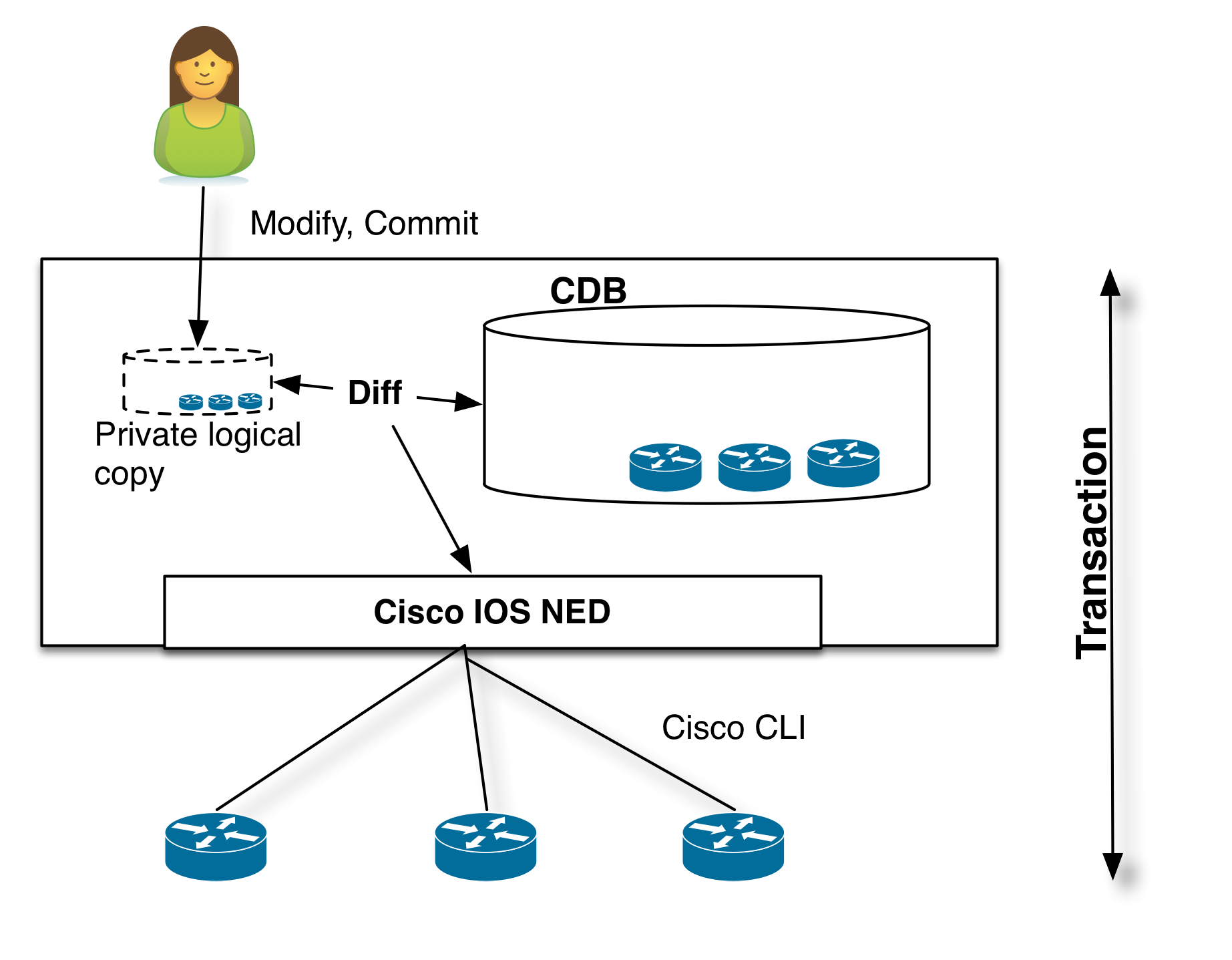
The modus operandi when using NSO to perform configuration changes is that the network engineer uses NSO (CLI, WebUI, REST,...) to modify the representation in NSO CDB. The changes are committed to the network as a transaction that includes the actual devices. Only if all changes happens on the actual devices will it be committed to the NSO data-store. The transaction also covers the devices so if any of the devices participating in the transaction fails, NSO will roll-back the configuration changes on the all modified devices. This works even in the case of devices that do not natively support roll-back like Cisco IOS CLI.
-
NSO can detect out of band changes and reconcile them by either updating the CDB or modifying the configuration on the devices to reflect the currently stored configuration.
NSO only needs to be synchronized with the devices in the event of a change being made outside of NSO. Changes made using NSO will reflected in both the CDB and the devices. The following actions do not need to be taken:
-
Perform configuration change via NSO
-
Perform sync-from action
The above incorrect (or not necessary) sequence stems from the assumption that the NSO CLI speaks directly to the devices. This is not the case, the northbound interfaces in NSO modifies the configuration in the NSO data-store, NSO calculates a minimum difference between current configuration and the new configuration, gives only the changes to the configuration to the NEDS that runs the commands to the devices. All this as one single change-set.
View the configuration of the "c0" device using the command:
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device c0 config
devices device c0
config
no ios:service pad
ios:ip vrf my-forward
bgp next-hop Loopback 1
!
...Or show a particular piece of configuration from several devices
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device c0..2 config ios:router
devices device c0
config
ios:router bgp 64512
aggregate-address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.251
neighbor 1.2.3.4 remote-as 1
neighbor 1.2.3.4 ebgp-multihop 3
neighbor 2.3.4.5 remote-as 1
neighbor 2.3.4.5 activate
neighbor 2.3.4.5 capability orf prefix-list both
neighbor 2.3.4.5 weight 300
!
!
!
devices device c1
config
ios:router bgp 64512
...Or show a particular piece of configuration from all devices
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device config ios:routerThe CLI can pipe commands, try TAB after "|" to see various pipe targets.
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device config ios:router \
| display xml | save router.xml
The above command shows the router config of all devices as
xml and then saves it to a file router.xml
In order to change the configuration, enter configure mode:
admin@ncs# config
Entering configuration mode terminal
admin@ncs(config)#Change or add some configuration across the devices, for example:
admin@ncs(config)# devices device c0..2 config ios:router bgp 64512
neighbor 10.10.10.0 remote-as 64502
admin@ncs(config-router)#It is important to understand how NSO applies configuration changes to the network. At this point the changes are local to NSO, no configurations have been sent to the devices yet. Since the NSO Configuration Database, CDB, is in sync with the network, NSO can calculate the minimum diff to apply the changes to the network. The command below compares the ongoing changes with the running database:
admin@ncs(config-router)#topadmin@ncs(config)#show configurationdevices device c0 config ios:router bgp 64512 neighbor 10.10.10.0 remote-as 64502 ...
It is possible to dry-run the changes in order to see the native Cisco CLI output (in this case almost the same as above):
admin@ncs(config)# commit dry-run outformat native
native {
device {
name c0
data router bgp 64512
neighbor 10.10.10.0 remote-as 64502
!
...The changes can be committed to the devices and the NSO CDB simultaneously with a single commit. In the commit command below, we pipe to details to understand the actions being taken.
admin@ncs% commit | detailsChanges are committed to the devices and the NSO database as one transaction. If any of the device configurations fail, all changes will be rolled back and the devices will be left in the state that they were in prior to the commit and the NSO CDB will not be updated. There are numerous options to the commit command which will affect the behaviour of the atomic transactions.
admin@ncs(config)# commit TAB
Possible completions:
and-quit Exit configuration mode
check Validate configuration
comment Add a commit comment
commit-queue Commit through commit queue
label Add a commit label
no-confirm No confirm
no-networking Send nothing to the devices
no-out-of-sync-check Commit even if out of sync
no-overwrite Do not overwrite modified data on the device
no-revision-drop Fail if device has too old data model
save-running Save running to file
---
dry-run Show the diff but do not perform commit
As seen by the details output, NSO stores a roll-back file for every commit so that the whole transaction can be rolled back manually. The following is an example of a roll-back file:
admin@ncs(config)#do file show logs/rollback1000Possible completions: rollback10001 rollback10002 rollback10003 \ rollback10004 rollback10005 admin@ncs(config)#do file show logs/rollback10005# Created by: admin # Date: 2014-09-03 14:35:10 # Via: cli # Type: delta # Label: # Comment: # No: 10005 ncs:devices { ncs:device c0 { ncs:config { ios:router { ios:bgp 64512 { delete: ios:neighbor 10.10.10.0; } } } }
(Viewing files as an operational command, prefixing a command in configuration mode with do executes in operational mode.) To perform a manual roll-back first load the rollback file:
admin@ncs(config)# rollback-files apply-rollback-file fixed-number 10005apply-rollback-file by default restores to that saved configuration, adding selective as parameter allows you to just rollback the delta in that specific rollback file. Show the differences:
admin@ncs(config)# show configuration
devices device c0
config
ios:router bgp 64512
no neighbor 10.10.10.0 remote-as 64502
!
!
!
devices device c1
config
ios:router bgp 64512
no neighbor 10.10.10.0 remote-as 64502
!
!
!
devices device c2
config
ios:router bgp 64512
no neighbor 10.10.10.0 remote-as 64502
!
!
!Commit the rollback:
admin@ncs(config)# commit
Commit complete.
A trace log can be created to see what is going on between NSO and the device CLI enable trace. Use the following command to enable trace:
admin@ncs(config)#devices global-settings trace raw trace-dir logsadmin@ncs(config)#commitCommit complete. admin@ncs(config)#devices disconnect
Note: Trace settings only take effect for new connections so is important to disconnect the current connections. Make a change to for example c0:
admin@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config ios:interface FastEthernet 1/2 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0admin@ncs(config-if)#commit dry-run outformat nativeadmin@ncs(config-if)#commit
Note the use of the command commit dry-run outformat native . This will display the net result device commands that will be generated over the native interface without actually committing them to the CDB or the devices. In addition there is the possibility to append the reverse flag that will display the device commands for getting back to the current running state in the network if the commit is successfully executed. Exit from the NSO CLI and return to the Unix Shell. Inspect the CLI trace:
less logs/ned-cisco-ios-c0.trace
As seen above, ranges can be used to send configuration commands towards several devices. Device groups can be created to allow for grouped actions that does not require naming conventions. A group can reference any number of devices. A device can be part of any number of groups, and groups can be hierarchical.
The command sequence below creates a group of core devices and a group with all devices. Note that you can use tab completion when adding the device names into the group. Also note that it requires configuration mode. (If you are still in the Unix Shell from the steps above, do $ncs_cli -C -u admin)
admin@ncs(config)#devices device-group core device-name [ c0 c1 ]admin@ncs(config-device-group-core)#commitadmin@ncs(config)#devices device-group all device-name c2 device-group coreadmin@ncs(config-device-group-all)#commitadmin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices device-groupdevices device-group all device-name [ c2 ] device-group [ core ] ! devices device-group core device-name [ c0 c1 ] ! admin@ncs(config)#do show devices device-groupNAME MEMBER INDETERMINATES CRITICALS MAJORS MINORS WARNINGS ------------------------------------------------------------------------- all [ c0 c1 c2 ] 0 0 0 0 0 core [ c0 c1 ] 0 0 0 0 0
Note well the "do show" which shows the operational data for the groups. Device groups has a member attribute that shows all member devices, flattening any group members.
Device groups can contain different devices as well as devices from different vendors. Configuration changes will be committed to each device in its native language without needing to be adjusted in NSO.
You can for example at this point use the group to check if all core are in sync:
admin@ncs# devices device-group core check-sync
sync-result {
device c0
result in-sync
}
sync-result {
device c1
result in-sync
}
Assume we would like to manage permit lists across devices.
This can be achieved by defining templates and apply them to device
groups. The following CLI sequence defines a tiny template, called
community-list :
admin@ncs(config)#devices template community-list ned-id cisco-ios-cli-3.0 config ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit permit-list 64000:40admin@ncs(config-permit-list-64000:40)#commitCommit complete. admin@ncs(config-permit-list-64000:40)#topadmin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices templatedevices template community-list config ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit permit-list 64000:40 ! ! ! ! [ok][2013-08-09 11:27:28]
This can now be applied to a device group:
admin@ncs(config)#devices device-group core apply-template \ template-name community-listadmin@ncs(config)#show configurationdevices device c0 config ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit 64000:40 ! ! devices device c1 config ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit 64000:40 ! ! admin@ncs(config)#commit dry-run outformat nativenative { device { name c0 data ip community-list standard test1 permit 64000:40 } device { name c1 data ip community-list standard test1 permit 64000:40 } } admin@ncs(config)#commitCommit complete.
What if the device group core contained different
vendors? Since the configuration is written in IOS the
above template would not work Juniper devices. Templates can
be used on different device types (read NEDs) by
using a prefix for the device model.
The template would then look like:
template community-list {
config {
junos:configuration {
...
}
ios:ip {
...
}
The above indicates how NSO manages different models for different device-types. When NSO connects to the devices the NEDs checks the device type and revision and returns that to NSO. This can be inspected (note, in operational mode):
admin@ncs# show devices device module
NAME NAME REVISION FEATURES DEVIATIONS
-------------------------------------------------------------------
c0 tailf-ned-cisco-ios 2014-02-12 - -
tailf-ned-cisco-ios-stats 2014-02-12 - -
c1 tailf-ned-cisco-ios 2014-02-12 - -
tailf-ned-cisco-ios-stats 2014-02-12 - -
c2 tailf-ned-cisco-ios 2014-02-12 - -
tailf-ned-cisco-ios-stats 2014-02-12 - -
So here we see that c0 uses a tailf-ned-cisco-ios
module which tells NSO which data-model to use for the device. Every NED package
comes with a YANG data-model for the device (except for third party YANG NED for which
YANG device model must be downloaded and fixed before it can be used). This renders the NSO
data-store (CDB) schema, the NSO CLI, WebUI and southbound commands.
The model introduces namespace prefixes for every configuration item. This also resolves issues around different vendors using the same configuration command for different configuration elements. Note that every item is prefixed with ios:
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device c0 config ios:ip community-list
devices device c0
config
ios:ip community-list 1 permit
ios:ip community-list 2 deny
ios:ip community-list standard s permit
ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit 64000:40
!
!
Another important question is how to control if the template shall
merge the list or replace the list. This is managed via "tags".
The default behavior of templates is to merge the configuration.
Tags can be inserted at any point in the template. Tag values are
merge, replace, delete,
create and nocreate.
Assume that c0 has the following configuration:
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device c0 config ios:ip community-list
devices device c0
config
ios:ip community-list 1 permit
ios:ip community-list 2 deny
ios:ip community-list standard s permit}If we apply the template the default result would be:
admin@ncs# show running-config devices device c0 config ios:ip community-list
devices device c0
config
ios:ip community-list 1 permit
ios:ip community-list 2 deny
ios:ip community-list standard s permit
ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit 64000:40
!
!
We could change the template in the following way to get a result where the permit list would be replaced rather than merged. When working with tags in templates it is often helpful to view the template as a tree rather then a command view. The CLI has a display option for showing a curly-braces tree view that corresponds to the data-model structure rather then the command set. This makes it easier to see where to add tags.
admin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices templatedevices template community-list config ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit permit-list 64000:40 ! ! ! ! admin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices \ template | display curly-bracestemplate community-list { config { ios:ip { community-list { standard test1 { permit { permit-list 64000:40; } } } } } } admin@ncs(config)#tag add devices template community-list ned-id cisco-ios-cli-3.0 config ip community-list replaceadmin@ncs(config)#commitCommit complete. admin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices template | display curly-bracestemplate community-list { config { ios:ip { /* Tags: replace */ community-list { standard test1 { permit { permit-list 64000:40; } } } } } }
Different tags can be added across the template tree.
If we now apply the template to device c0 which already
have community lists the following happens:
admin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices device c0 \ config ios:ip community-listdevices device c0 config ios:ip community-list 1 permit ios:ip community-list 2 deny ios:ip community-list standard s permit ios:ip community-list standard test1 permit 64000:40 ! ! admin@ncs(config)#devices device c0 apply-template \ template-name community-listadmin@ncs(config)#show configurationdevices device c0 config no ios:ip community-list 1 permit no ios:ip community-list 2 deny no ios:ip community-list standard s permit ! !
Any existing values in the list are replaced in this case. The following tags are available:
-
merge (default): the template changes will be merged with the existing template
-
replace: the template configuration will be replaced by the new configuration
-
create: the template will create those nodes which does not exist. If a node already exists this will result in an error.
-
nocreate: the merge will only affect configuration items that already exist in the template. It will never create the configuration with this tag, or any associated commands inside it. It will only modify existing configuration structures.
-
delete: delete anything from this point
Note that a template can have different tags along the tree nodes.
A "problem" with the above template is that every value is hard-coded. What if you wanted a template where the community-list name and permit-list value are variables passed to the template when applied? Any part of a template can be a variable, (or actually an XPATH expression). We can modify the template to use variables in the following way:
admin@ncs(config)#no devices template community-list config ios:ip \ community-list standard test1admin@ncs(config)#devices template community-list config ios:ip \ community-list standard \ {$LIST-NAME} permit permit-list {$AS}admin@ncs(config-permit-list-{$AS})#commitCommit complete. admin@ncs(config-permit-list-{$AS})#topadmin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices templatedevices template community-list config ios:ip community-list standard {$LIST-NAME} permit permit-list {$AS} ! ! ! !
The template now requires two parameters when applied (tab completion will prompt for the variable):
admin@ncs(config)#devices device-group all apply-template template-name community-list variable { name LIST-NAME value 'test2' } variable { name AS value '60000:30' }admin@ncs(config)#commit
Note, that the replace tag was still part of the
template and it would delete any existing community lists,
which is probably not the desired outcome in the general case.
The template mechanism described so far is
"fire-and-forget". The templates do not have any
memory of what happened to the network, which devices they
touched. A user can modify the templates without anything
happening to the network until an explicit
apply-template action is performed. (Templates are
of course as all configuration changes done as a transaction).
NSO also supports service templates that are more
"advanced" in many ways, more information on this will
be presented later in this guide.
Also note that device templates have some additional restrictions on the values that can be supplied when applying the template. In particular, a value must either be a number or a single-quoted string. It is currently not possible to specify a value that contains a single quote (').
In order to make sure that configuration is applied according to site or corporate rules you can use policies. Policies are validated at every commit, they can be of type error that implies that the change cannot go through or a warning which means that you have to confirm a configuration that gives a warning.
A policy is composed of:
-
Policy name
-
Iterator: loop over a path in the model, for example all devices, all services of a specific type.
-
Expression: a boolean expression that must be true for every node returned from the iterator, for example, snmp must be turned on.
-
Warning or error: a message displayed to the user. If it is of type warning the user can still commit the change, if of type error the change cannot be made.
An example is shown below:
admin@ncs(config)#policy rule class-mapPossible completions: error-message Error message to print on expression failure expr XPath 1.0 expression that returns a boolean foreach XPath 1.0 expression that returns a node set warning-message Warning message to print on expression failure admin@ncs(config)#policy rule class-map foreach /devices/device \ expr config/ios:class-map[name='a'] \ warning-message "Device {name} must have a class-map a"admin@ncs(config-rule-class-map)#topadmin@ncs(config)#commitCommit complete. admin@ncs(config)#show full-configuration policypolicy rule class-map foreach /devices/device expr config/ios:class-map[ios:name='a'] warning-message "Device {name} must have a class-map a" !
Now if we try to delete a class-map 'a' we will get a policy violation.
admin@ncs(config)#no devices device c2 config ios:class-map match-all aadmin@ncs(config)# validate Validation completed with warnings: Device c2 must have a class-map a admin@ncs(config)#commitThe following warnings were generated: Device c2 must have a class-map a Proceed? [yes,no] yes Commit complete. admin@ncs(config)#validateValidation completed with warnings: Device c2 must have a class-map a
The {name} variable refers to the node-set from the iterator. This node-set will be the list of devices in NSO and the devices have an attribute called 'name'.
In order to understand the syntax for the expressions a pipe-target in the CLI can be used:
admin@ncs(config)# show full-configuration devices device c2 config \
ios:class-map | display xpath
/ncs:devices/ncs:device[ncs:name='c2']/ncs:config/ \
ios:class-map[ios:name='cmap1']/ios:prematch match-all
...
In order to debug policies look at the end of
logs/xpath.trace.
This file will show all validated XPATH expressions and any
errors.
4-Sep-2014::11:05:30.103 Evaluating XPath for policy: class-map:
/devices/device
get_next(/ncs:devices/device) = {c0}
XPath policy match: /ncs:devices/device{c0}
get_next(/ncs:devices/device{c0}) = {c1}
XPath policy match: /ncs:devices/device{c1}
get_next(/ncs:devices/device{c1}) = {c2}
XPath policy match: /ncs:devices/device{c2}
get_next(/ncs:devices/device{c2}) = false
exists("/ncs:devices/device{c2}/config/class-map{a}") = true
exists("/ncs:devices/device{c1}/config/class-map{a}") = true
exists("/ncs:devices/device{c0}/config/class-map{a}") = true
Validation scripts can also be defined in Python, see more about that in "Plug and Play scripts".
In reality, network engineers will still modify configurations
using other tools like out of band CLI or other management interfaces.
It is important to understand how does NSO manage this.
The NSO network simulator supports CLI towards the devices.
For example we can use the IOS CLI on say c0 and
delete a permit-list. From the UNIX shell start
a CLI session towards c0.
$ncs-netsim cli-i c0c0>enablec0#configureEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. c0(config)#show full-configuration ip community-listip community-list standard test1 permit ip community-list standard test2 permit 60000:30 c0(config)#no ip community-list standard test2c0(config)# c0# exit $
Start the NSO CLI again:
$ ncs_cli -C -u adminNSO detects if its configuration copy in CDB differs from the configuration in the device. Various strategies are used depending on device support; transaction-ids, time-stamps, configuration hash-sums. For example a NSO user can request a check-sync operation:
admin@ncs#devices check-syncsync-result { device c0 result out-of-sync info got: e54d27fe58fda990797d8061aa4d5325 expected: 36308bf08207e994a8a83af710effbf0 } sync-result { device c1 result in-sync } sync-result { device c2 result in-sync } admin@ncs#devices device-group core check-syncsync-result { device c0 result out-of-sync info got: e54d27fe58fda990797d8061aa4d5325 expected: 36308bf08207e994a8a83af710effbf0 } sync-result { device c1 result in-sync }
NSO can also compare the configurations with the CDB and show the difference:
admin@ncs# devices device c0 compare-config
diff
devices {
device c0 {
config {
ios:ip {
community-list {
+ standard test1 {
+ permit {
+ }
+ }
- standard test2 {
- permit {
- permit-list 60000:30;
- }
- }
}
}
}
}
}At this point we can choose if we want to use the configuration stored in the CDB as the valid configuration or the configuration on the device:
admin@ncs#devices sync-Possible completions: sync-from Synchronize the config by pulling from the devices sync-to Synchronize the config by pushing to the devices admin@ncs#devices sync-to
In the above example we chose to overwrite the device configuration from NSO.
NSO will also detect out-of-sync when committing changes. In
the following scenario a local c0 CLI user adds
an interface. Later a NSO user tries to add an interface:
$ncs-netsim cli-i c0c0>enablec0#configureEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. c0(config)#interface FastEthernet 1/0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0c0(config-if)# c0# exit $ncs_cli -C -u adminadmin@ncs#configEntering configuration mode terminal admin@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config ios:interface \ FastEthernet1/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0admin@ncs(config-if)#commitAborted: Network Element Driver: device c0: out of sync
At this point we actually have two diffs:
-
The device and NSO CDB (devices device compare-config)
-
The on-going transaction and CDB (show configuration)
admin@ncs(config)#devices device c0 compare-configdiff devices { device c0 { config { ios:interface { FastEthernet 1/0 { ip { address { primary { + mask 255.255.255.0; + address 192.168.1.1; } } } } } } } } admin@ncs(config)#show configurationdevices device c0 config ios:interface FastEthernet1/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 exit ! !
To resolve this you can choose to synchronize the configuration between the devices and the CDB before committing. There is also an option to over-ride the out-of-sync check:
admin@ncs(config)# commit no-out-of-sync-checkor:
admin@ncs(config)# devices global-settings out-of-sync-commit-behaviour
Possible completions:
accept reject
As noted before, all changes are applied as complete transactions of all configurations on all of the devices. Either all configuration changes are completed successfully or all changes are removed entirely. Consider a simple case where one of the devices is not responding. For the transaction manager an error response from a device or a non-responding device are both errors and the transaction should automatically rollback to the state before the commit command was issued.
Stop c0:
$ ncs-netsim stop c0 DEVICE c0 STOPPED
Go back to the NSO CLI and perform a configuration change over c0 and c1:
admin@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config ios:ip community-list \ standard test3 permit 50000:30admin@ncs(config-config)#devices device c1 config ios:ip \ community-list standard test3 permit 50000:30admin@ncs(config-config)#topadmin@ncs(config)#show configurationdevices device c0 config ios:ip community-list standard test3 permit 50000:30 ! ! devices device c1 config ios:ip community-list standard test3 permit 50000:30 ! ! admin@ncs(config)#commitAborted: Failed to connect to device c0: connection refused: Connection refused admin@ncs(config)# *** ALARM connection-failure: Failed to connect to device c0: connection refused: Connection refused
NSO sends commands to all devices in parallel, not sequentially. If any of the devices fails to accept the changes or reports an error, NSO will issue a rollback to the other devices. Note, this works also for non-transactional devices like IOS CLI and SNMP. This works even for non-symmetrical cases where the rollback command sequence is not just the reverse of the commands. NSO does this by treating the rollback as it would any other configuration change. NSO can use the current configuration and previous configuration and generate the commands needed to rollback from the configuration changes.
The diff configuration is still in the private CLI session, it can be restored, modified (if the error was due to something in the config), or in some cases, fix the device.
NSO is not a "best effort" configuration management system. The error reporting coupled with the ability to completely rollback failed changes to the devices, ensures that the configurations stored in the CDB and the configurations on the devices are always consistent and that no failed or "orphan" configurations are left on the devices.
First of all, if the above was not a multi-device transaction, meaning that the change should be applied independently device per device, then it is just a matter of performing the commit between the devices.
Second, NSO has a commit flag "commit-queue async" or "commit-queue sync". The commit queue should primarily be used for throughput reasons when doing configuration changes in large networks. Atomic transactions comes with a cost, the critical section of the database is locked when committing the transaction on the network. So, in cases where there are northbound systems of NSO that generates many simultaneous large configuration changes these might get queued. The commit queue will send the device commands after the lock has been released, so the database lock is much shorter. If any device fails an alarm will be raised.
admin@ncs(config)#commit commit-queue asynccommit-queue-id 2236633674 Commit complete. admin@ncs(config)#do show devices commit-queue | notabdevices commit-queue queue-item 2236633674 age 11 status executing kilo-bytes-size 1 devices [ c0 c1 c2 ] transient-errors [ c0 ] is-atomic true
Go to the UNIX shell and start the device and monitor the commit queue.
$ncs-netsim start c0DEVICE c0 OK STARTED $ncs_cli -C -u adminadmin@ncs#show devices commit-queuedevices commit-queue queue-item 2236633674 age 11 status executing kilo-bytes-size 1 devices [ c0 c1 c2 ] transient-errors [ c0 ] is-atomic true admin@ncs#show devices commit-queuedevices commit-queue queue-item 2236633674 age 11 status executing kilo-bytes-size 1 devices [ c0 c1 c2 ] is-atomic true admin@ncs#show devices commit-queue% No entries found.
Devices can also be pre-provisioned, this means that the configuration can be prepared in NSO and pushed to the device when it is available. To illustrate this we can start by adding a new device to NSO that is not available in the network simulator:
admin@ncs(config)#devices device c3 address 127.0.0.1 port 10030 \ authgroup default device-type cli ned-id cisco-iosadmin@ncs(config-device-c3)#state admin-state southbound-lockedadmin@ncs(config-device-c3)#commit
Above we added a new device to NSO with IP address local host
and port 10030. This device does not exist in the network
simulator. We can tell NSO not to send any commands
southbound by setting the admin-state to southbound-locked (actually the
default). This means that all configuration changes will
succeed, the result will be stored in CDB. At any point in
time when the device is available in the network the state can
be changed and the complete configuration pushed to the new
device. The CLI sequence below also illustrates a powerful
copy configuration command which can copy any configuration
from one device to another. The from and to paths are
separated by the keyword to.
admin@ncs(config)#copy cfg merge devices device c0 config \ ios:ip community-list to \ devices device c3 config ios:ip community-listadmin@ncs(config)#show configurationdevices device c3 config ios:ip community-list standard test2 permit 60000:30 ios:ip community-list standard test3 permit 50000:30 ! ! admin@ncs(config)#commitadmin@ncs(config)#devices check-sync... sync-result { device c3 result locked }
As shown above check-sync operations will tell
the user that the device is southbound locked. When the device
is available in the network the device can be synchronized
with the current configuration in the CDB using the sync-to
action.
Different users or management tools can of course run parallel sessions to NSO. All on-going sessions have a logical copy of CDB. An important case needs to be understood if there is a conflict when multiple users attempt to modify the same device configuration at the same time with different changes. First lets look at the CLI sequence below, user admin to the left, user joe to the right.
admin@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config ios:snmp-server community fozbarjoe@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config ios:snmp-server community fezbaradmin@ncs(config-config)#commitSystem message at 2014-09-04 13:15:19... Commit performed by admin via console using cli. joe@ncs(config-config)# commit joe@ncs(config)#show full-configuration devices device c0 config ios:snmp-serverdevices device c0 config ios:snmp-server community fezbar ios:snmp-server community fozbar ! !
There is no conflict in the above sequence, community is a list so both joe and admin can add items to the list. Note that user joe gets information about user admin committing.
On the other hand if two users modifies an ordered-by user list in such way that one user rearranges the list, along with other non-conflicting modifications, and one user deletes the entire list the following happens:
admin@ncs(config)#no devices device c0 config access-list 10joe@ncs(config)#move devices device c0 config access-list 10 permit 168.215.202.0 0.0.0.255 firstjoe@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config logging history informationaljoe@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config logging source-interface Vlan512joe@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config logging 10.1.22.122joe@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config logging 66.162.108.21joe@ncs(config)#devices device c0 config logging 50.58.29.21admin@ncs%commitSystem message at 2022-09-01 14:17:59... Commit performed by admin via console using cli. joe@ncs(config-config)#commitAborted: Transaction 542 conflicts with transaction 562 started by user admin: 'devices device c0 config access-list 10' read-op on-descendant write-op delete in work phase(s) -------------------------------------------------------------------------- This transaction is in a non-resolvable state. To attempt to reapply the configuration changes made in the CLI, in a new transaction, revert the current transaction by running the command 'revert' followed by the command 'reapply-commands'. --------------------------------------------------------------------------
In this case joe commits a change to
access-list after admin and a conflict
message is displayed. Since the conflict is non-resolvable the transaction has to be reverted.
In order to reapply the changes made by joe to logging in a new transaction, the following commands are entered:
joe@ncs(config)#revert no-confirmjoe@ncs(config)#reapply-commands best-effortmove devices device c0 config access-list 10 permit 168.215.202.0 0.0.0.255 first Error: on line 1: move devices device c0 config access-list 10 permit 168.215.202.0 0.0.0.255 first devices device c0 config logging history informational logging facility local0 logging source-interface Vlan512 logging 10.1.22.122 logging 66.162.108.21 logging 50.58.29.21 joe@ncs(config-config)#show configlogging facility local0 logging history informational logging 10.1.22.122 logging 50.58.29.21 logging 66.162.108.21 logging source-interface Vlan512 joe@ncs(config-config)#commitCommit complete.
In this case joe tries to reapply the changes made in the previous transaction and since access-list 10 has been removed, the move command will fail when applied by the reapply-commands command. Since the mode is best-effort the next command will be processed. The changes to logging will succeed and joe then commits the transaction.