Ansible provides a clean way to accomplish the creation and removal of VLANs because Ansible doesn’t require an agent be installed on the devices. The main requirements for this solution are:
- SSH
- Python – this is not required, but it is the most commonly used language
In this particular example we are going to demonstrate how to leverage Ansible to create VLANs. Below is a graphical representation of how Ansible relates to the network.
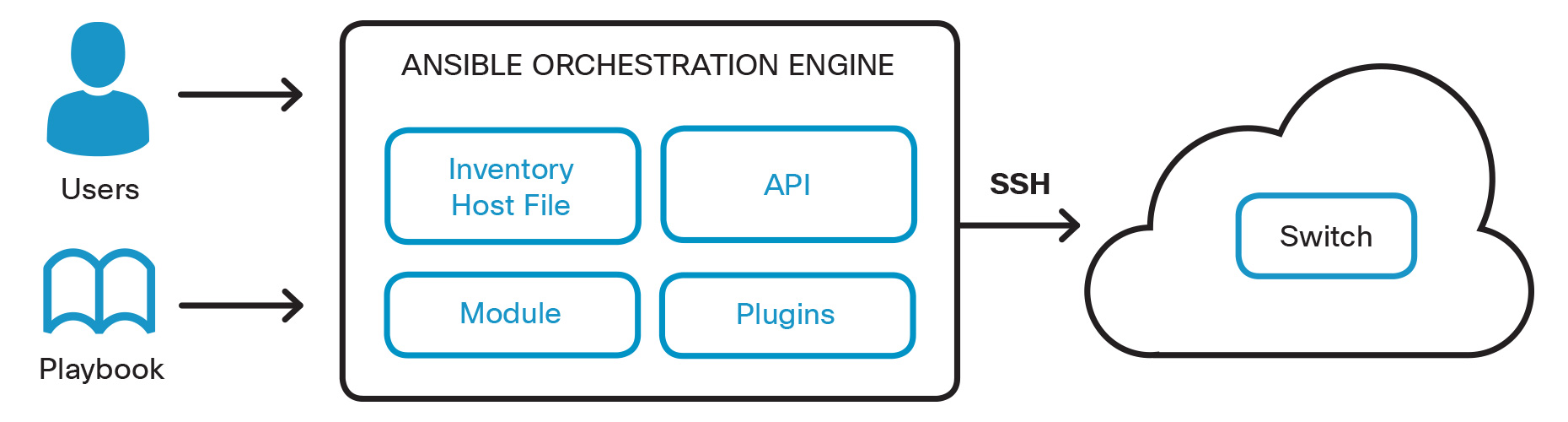
Ansible Workflow with a Cisco Open NX-OS Switch
To understand the solution approach, it might be beneficial to understand some of the key Ansible terminology:
- Hosts: Remote machines Ansible manages.
- Groups: Group of hosts assigned to a pool that can be conveniently targeted and managed together.
- Inventory: File describing the Hosts and Groups in Ansible.
- Modules: Modules (also referred to as "task plugins" or "library plugins") are the components that do the actual work in Ansible. They are what gets executed in each playbook task.
- Playbooks: A collection of plays which the Ansible Engine orchestrates, configures, administers, or deploys. These playbooks describe the policy to be executed to the host(s). People refer to these playbooks as "design plans" which are designed to be human-readable and are developed in a basic text language called YAML.