In Open NX-OS, network interfaces are exposed as netdevices within Linux (EthX-X). Linux commands a network operator can use are ifconfig, tcpdump, vsh etc. to make it easier to manage the switch interfaces in the same manner as network ports on a Linux server.
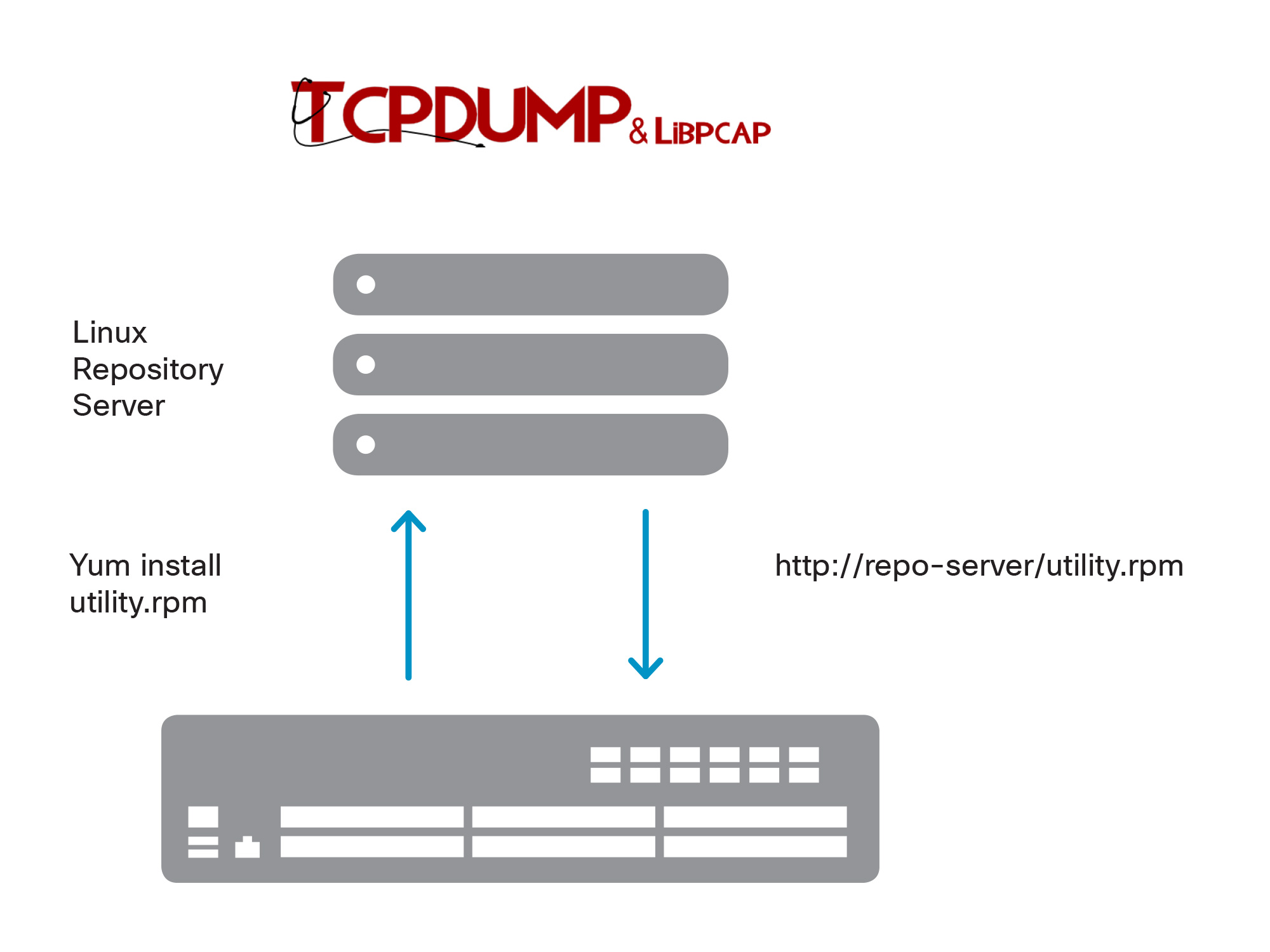
Using Standard Package Management Infrastructure (for example, yum) with Open NX-OS
For troubleshooting, use tcpdump to capture all packets on a given port, and dump output to a file:
bash-4.2$ sudo tcpdump -w file.pcap -i Eth1-1
tcpdump: WARNING: Eth1-1: no IPv4 address assigned
tcpdump: listening on Eth1-1, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes
3 packets captured
3 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
Use ethtool to display detailed interface statistics:
#ethtool –S eth1-1
NIC statistics:
speed: 10000
port_delay: 10
port_bandwidth: 10000000
admin_status: 1
oper_status: 1
port_mode: 0
reset_counter: 20
load-interval-1: 30
rx_bit_rate1: 0
rx_pkt_rate1: 0
tx_bit_rate1: 272
tx_pkt_rate1: 0
load-interval-2: 300
rx_bit_rate2: 0
rx_pkt_rate2: 0
tx_bit_rate2: 256
tx_pkt_rate2: 0
rx_unicast_pkts: 1340
rx_multicast_pkts: 0
rx_broadcast_pkts: 0
rx_input_pkts: 1340
rx_bytes_input_pkts: 1886720
Verify the MTU of an interface, and then use ifconfig to change mtu for an interface to jumbo MTU:
n9k-sw-1# run bash
bash-4.2#
bash-4.2# ifconfig Eth1-1
Eth1-1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet6 fe80::fac2:88ff:fe90:2cb2 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether f8:c2:88:90:2c:b2 txqueuelen 100 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2204374 bytes 170123906 (162.2 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
The following example shows how to set the MTU for interface 1/1 to 9000
bash-4.2# sudo ifconfig Eth1-1 mtu 9000
bash-4.2#
bash-4.2# ifconfig Eth1-1
Eth1-1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr f8:c2:88:90:2c:b2
inet6 addr: fe80::fac2:88ff:fe90:2cb2/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:9000 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:2204856 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:170161160 (162.2 MiB)
The last example depicts how customers can execute NX-OS commands from bash. This is beneficial because the user will be able to execute commands and leverage their existing Linux tools to manage the switch. In this particular example, we are querying the interfaces from the switch leveraging the vsh command from bash shell.
bash-4.2$ vsh -c "show interface brief" | grep up | awk '{print $1}'
mgmt0
Eth1/49
bash-4.2$