Communication
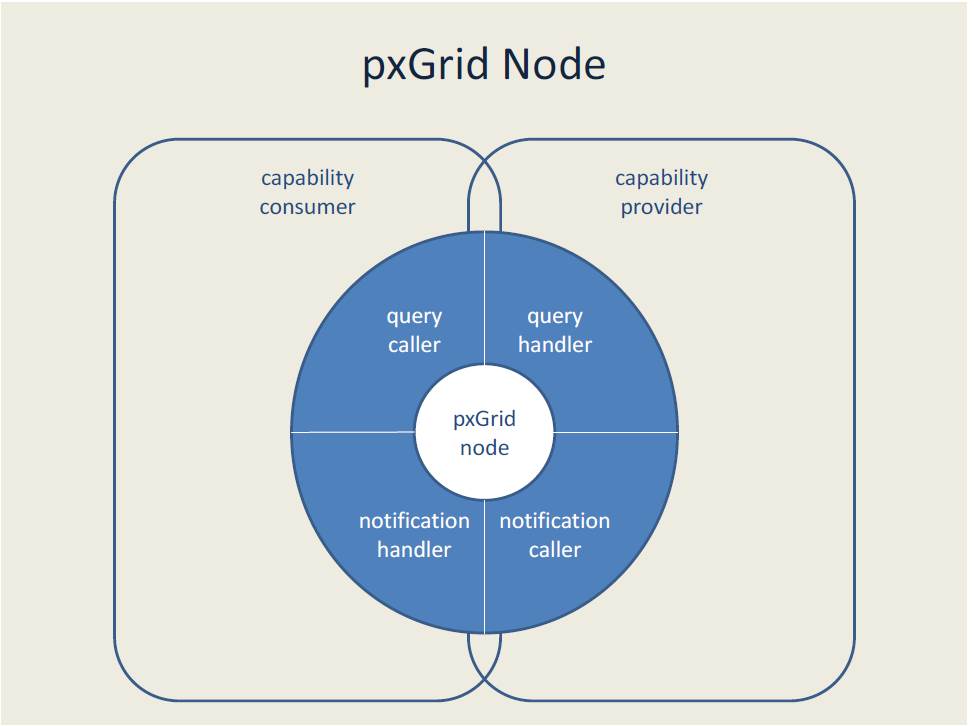
With a model in place, pxGrid enables communication between pxGrid nodes. Nodes can be both providers and consumers of capabilities. As the provider of a capability, a node handles queries, generates notifications, or both. As the consumer of a capability, a node initiates queries, receives notifications, or both. The figure below shows the anatomy of a pxGrid node and breaks down a node's communication capabilities.
Node Registration
Before a node can communicate with pxGrid, it needs to be registered in pxGrid. pxGrid allows auto registration of nodes based on certificates. When a pxGrid node connects to pxGrid the first time, the node is registered and allowed to communicate over pxGrid if the certificates are valid. The access level of the pxGrid node is governed by the authorization group that the node is part of. pxGrid also supports restricted manual registration mode wherein each new node must be approved by an administrator and assigned an authorization group to communicate over pxGrid. Once a node is registered, it is allowed to be a provider or consumer of a capability only if it has the required authorization for that capability.
Auto registration mode can be used if the deployment is a secure or closed deployment. In an open deployment where security is a concern, manual node registration mode is recommended.
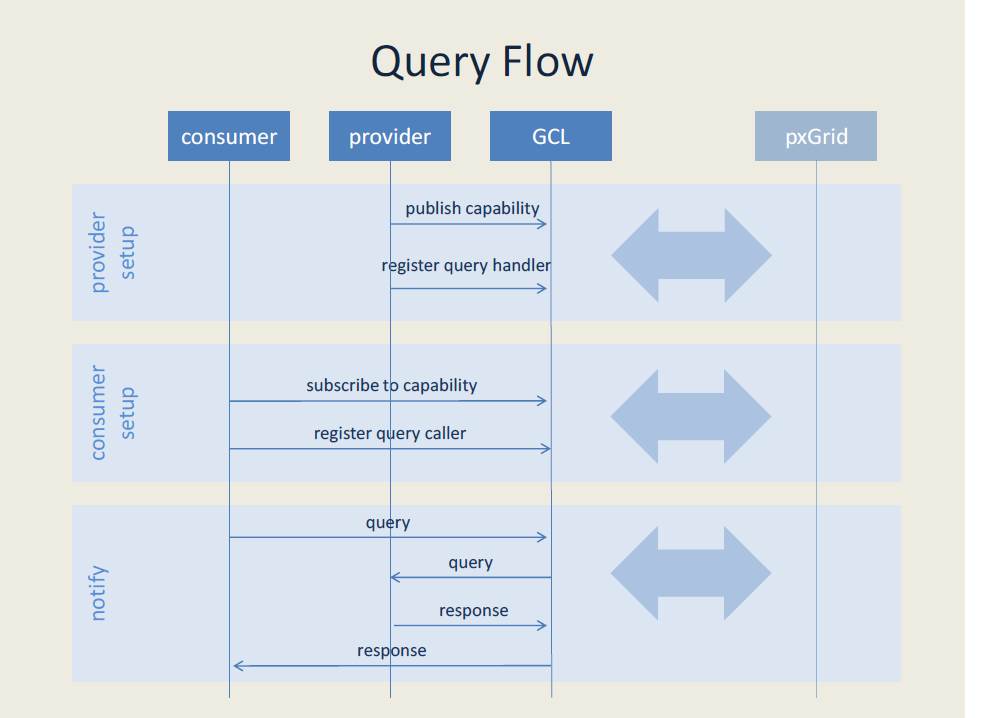
Query
A query is a synchronous call initiated by a consumer and serviced by a provider. Using the GCL, the consumer utilizes a query caller to initiate the communication. The provider implements a query handler to programmatically process requests and generate responses. pxGrid passes the request through the consumer GCL and into the provider GCL, likely on another node in the network. Using custom code implemented by the developer in a query handler, the provider generates a response that pxGrid then sends back to the consumer. The consumer waits until the response is received.
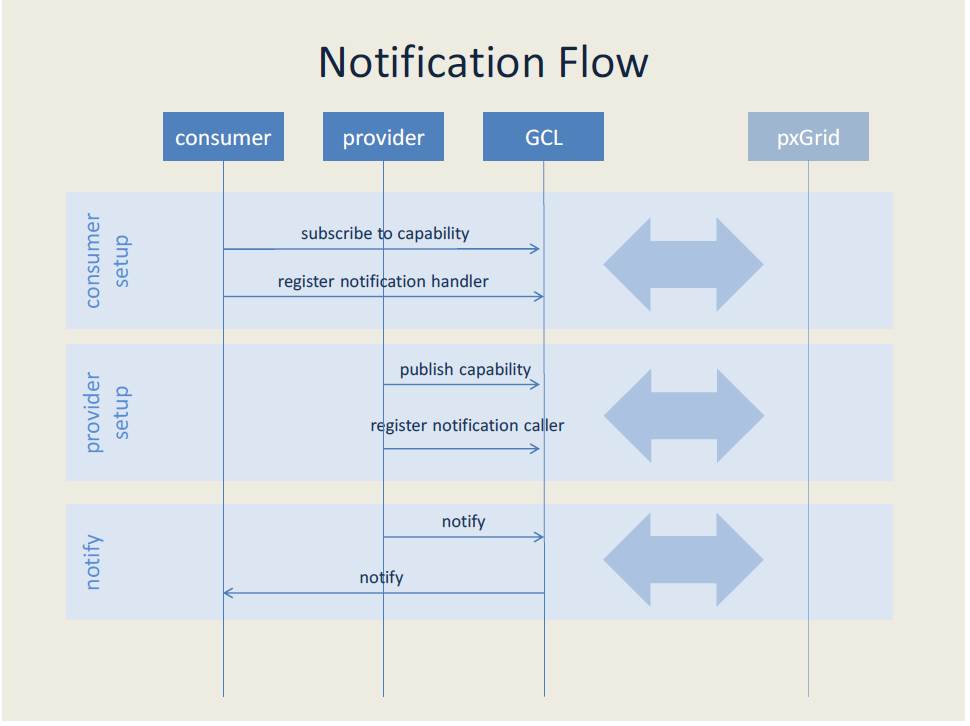
Notification
A notification is an asynchronous message generated by a provider and received by a consumer. The consumer must first register interest in a topic of information. Using messaging terminology, consumers subscribe to a topic and providers publish to the topic. The GCL handles communication with pxGrid so the consumers and providers can focus on writing code to consume and provide the information. Unlike in the query flow, consumers do not wait for information. The GCL uses a separate thread to invoke a notification handler supplied by the consumer. The figure below details the flow.