Authentication
Starting from release 20.18.1, Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager supports JSON web token (JWT) authentication for REST API access control. For a general discussion on JWT, see IETF RFC 7519. Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager continues to support session-based authentication using JSESSIONIDs to ensure backward compatibility.
The following sections describe the two authentication methods:
- JWT-based authentication
- Session-based authentication
JWT-based Authentication
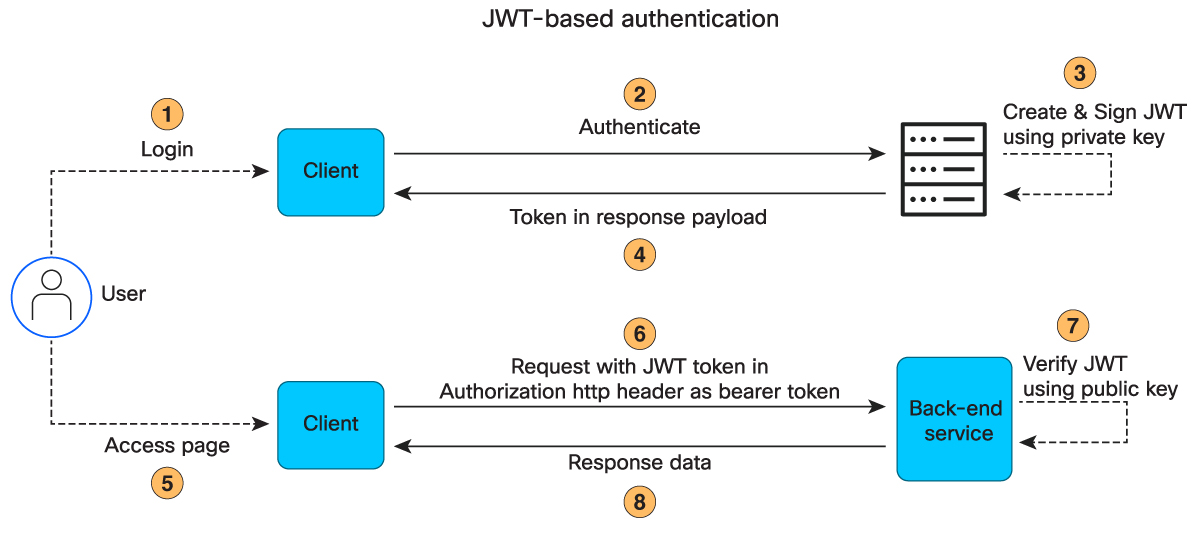
Log in with a Username and Password
Log in with a username and password to receive a JWT token (referred as the access token in this document):
POST /jwt/login with content type application/json in the request header. Submit the mandatory "username" and "password" attributes, along with an optional "duration" attribute, expressed in seconds, for the access token in the POST request body. The default expiration duration for the access token is 1,800 seconds (30 minutes). Here is an example:
curl -X POST \
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/jwt/login" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
"username": "<String containing a username>",
"password": "<String containing a password>",
"duration": "<Optional duration of range in seconds from 1 to 604800 (7 days)>"
}"
POST https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address>:8443/jwt/login
HTTP Request Header:
{'Content-Type: application/json'}
HTTP Request Body:
{
'username': '<String containing a username>',
'password': '<String containing a password>',
'duration': <Optional integer duration of range in seconds from 1 to 604800 (7 days)>
}
When user authentication is successful, the response body contains a JSON object. Here is an example:
HTTP Response Body:
{
"token": "<String containing the access token>",
"refresh": "<String containing the refresh token>",
"sub": "<Optional case-sensitive string identifying the principal that is the subject of the JWT. See RFC 7519>",
"iss": "<Optional case-sensitive string containing the principal that issued the JWT. See RFC 7519>",
"aud": "<Optional case-sensitive string identifying the recipients the JWT is intended for. See RFC 7519>",
"userGroup": "<String containing the SD-WAN Manager usergroup/role to which the userid belongs>",
"tenant": "<String containing the SD-WAN Manager tenant name to which the userid belongs>",
"duration": <Integer indicating the expiration duration of the access token in seconds>,
"exp": <Integer indicating the expiration time on or after which the JWT must not be accepted. See RFC 7519>
"csrf": "<String containing a cross-site request forgery token, required for most POST actions>",
"isAPIKey": <Boolean, indicating whether the access token is intended as a long-lived API key. Defaults to false>
"tenantId": "<String containing the SD-WAN Manager tenant ID>"
}
If a user fails to authenticate successfully, the system returns an HTTP 401 error.
Within the JSON object, you can retrieve the access token through the "token" claim within the response body. The "csrf" claim contains a cross-site request forgery (XSRF) prevention token, which is necessary for most POST operations. Hence, for the JWT-based authentication method, there is no need for a separate API call to GET /dataservice/client/token to retrieve the XSRF token.
Use the access token along with the XSRF token for further API requests.
Example of response:
{
"token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJqd3QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJqYmFyb3pldCIsdbaUpImlzcyI6IjNhOWEyN2VhLWQxNWUtNDEwNC05YjQxLTdiMGE5ZWExZWFjOSIsImF1ZCI6InZtYW5hZ2UiLCJ1c2VyR3JvdXAiOiJbbmV0YWRtaW5dIiwidGVuYW50IjoiTWFya2V0aW5nLURlbW8iLCJkdXJhdGlvbiI6MzYwMCwiZXhwIjoxNzUzMDk2NzE2LCJjc3JmIjoiMEIxMTAyOERQjA4RkYwOTIyQTEzOEMDlCMDczOEMyNzc5NTA2MDVBNjAyNkUwNzQ4MzVFMUVEM0NCRUQxNEJBNUQ1RDU0RTBFNTJS2V5IjpmYWxzZSwidGVuYW50SWQiOiJkZWZhdWx0In0.EMdhbdDhP3UmV34Ma8_7VNlIzfLy6gkznIBrvEeVsxCVKw2H_R-uhScs7nM9HmOi64gTsL5bS38db231aXS5_hW0U84dGgxN4dSxKG784fihlkpips9PF7n39L6N8fkqaO2UzmdtRf_FRnTIsWq1q3vmZJtAb1aMbp8MjmkRs06crcbSzQzGD2e35HgKfkNlNcnmLpvg9sxTY2QY0hjFoo3aXTmDzdlZvGY65QvXAah14zKkko8aiN30KDw",
"refresh": "eyJ0eXAiOiJqd3QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJqYmFyb3pldCIsImNzcmYiOiIwQjExMDI4RERFMzYzRTlCMDDY3OEQwOUIwNzM4QzI3Nzk1MDYwNUE2MDI2RTA3NDgzNUUxRUABDUQzQ0JFRDE0QkE1RDVENTRFMEU1MTI0IiwiZXhwIjoyMDY0MTMxNjI1LCJ0ZW5hbnRJZCI6ImRlZmF1bHQifQ.dpy-CipMvhSo30oqml6yrCtEK4_G-VRC1mgHCntS1HkVpaUMDoRiHdcBy7HTOscHqdMfpdkOH0cbZnlfV-pGWkiR3wSsO_euiCtAUwb58SOycu8wil83StrtUoZmD1uNJdClNFHWjuZOQSS0m0oEmjDLFuqL2dOB8_671UzJsPFJSPA__3gthayTTx3MxgMDeDoIXZZjRyFopTpUVHA6hEBJuAhiTvxA",
"sub": "admin",
"iss": "3a9a49ea-d15e-4406-9b51-7b0a9ea1eac9",
"aud": "vmanage",
"userGroup": "[netadmin]",
"tenant": "Demo",
"duration": 3600,
"exp": 1753096716,
"csrf": "0B11028DDAAB66DDE363E9B08FF0922A138B3AB640DBD697E1AD03220738C2779526E074835E1ED3CBED14BA5D5D54E0E5124",
"isAPIKey": false,
"tenantId": "default"
}
Make an API Request
For calls to API endpoints, you must provide the access token within the "Authorization" header of the HTTP request, in the form of a bearer token. For POST requests, you must also provide the matching XSRF token. Here is an example:
curl -X GET \
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/dataservice/device" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <JWT Token>" \
-H "X-XSRF-TOKEN: <XSRF "<XSRF Token>" \
-k
https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address>/dataservice/<some API endpoint URL>
HTTP Request Header:
{'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'Bearer <JWT token>', 'X-XSRF-TOKEN': '<XSRF token>'}
Refresh Expired Access Tokens
Apart from the access token, Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager also returns a refresh token. The refresh token is available in the "refresh" claim within the body of the POST /jwt/login API response. The system sets the refresh token expiration duration to one day multiplied by the duration of the access token. By default, the access token expires after 1,800 seconds. To calculate the refresh token expiration, multiply 86,400 by 1,800, resulting in 155,520,000 seconds or 1,800 days. Adjusting the access token’s expiration duration in the POST /jwt/login or POST /jwt/refresh API endpoints will also change the refresh token’s expiration accordingly.
You can use the refresh token to generate a new access token without presenting the userid and password credentials through the POST /jwt/refresh API endpoint as follows:
curl -X POST \
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/jwt/refresh" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
"refresh": "<Mandatory string containing the refresh token>",
"duration": "<Optional duration of range in seconds from 1 to 604800 (7 days)>"
}"
POST https://<SD-WAN Manager IP Address>:8443/jwt/refresh
HTTP Request Header:
{'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
HTTP Request Body:
{
'refresh': '<Mandatory string containing the refresh token>',
'duration': '<Optional integer duration of range in seconds from 1 to 604800 (7 days)>'
}
When you refresh an access token successfully, the response body contains a JSON object in the following form:
HTTP Response Body:
{
"token": "<String containing the access token>",
"refresh": "<String containing the refresh token>",
}
Note:
- The
POST /jwt/refreshAPI endpoint does not update the refresh token, so it cannot be refreshed. After the refresh token expires, obtain a new access and refresh token by submitting credentials to thePOST /jwt/login endpoint.- With the JWT-based authentication method, there is no API endpoint for logging out. Request the token with a short expiration time to ensure access and refresh tokens do not remain valid after completing requests to all necessary API endpoints.
Session-based Authentication
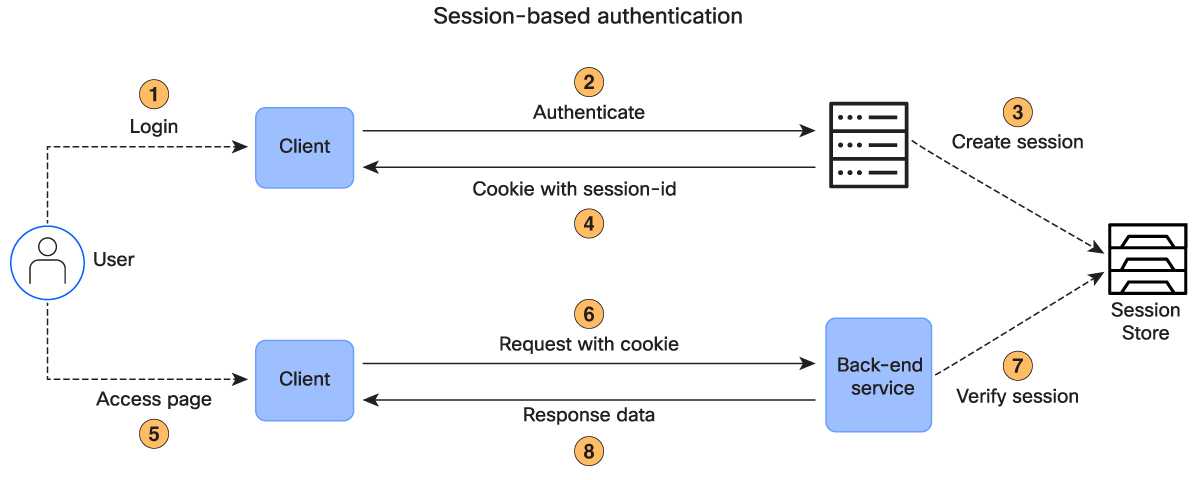
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager still supports the traditional REST API access control that is based on sessions (JSESSIONIDs). With this authentication method, Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager creates a session for each user after successful login.
Log in with a Username and Password to Establish a Session:
POST /j_security_check with content type x-www-form-urlencoded in the request header. Submit the username and password as j_username and j_password in the body of the POST request. See the following example.
curl -c cookie.text -X POST \
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/j_security_check" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "j_username=<username>&j_password=<password>"
POST https://<SD-WAN Manager IP Address>/j_security_check
HTTP Request Header:
{'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
HTTP Request Body:
{"j_username=<username>&j_password=<password>"}
When a user authenticates successfully, the response body is empty, but the response header includes a valid session cookie. The session token is in the response HTTP cookie, JSESSIONID=<session hash>. Here is an example:
HTTP Response Header: {
'set-cookie': 'JSESSIONID=<session hash>',
...Additional headers not shown...
}
If a user fails to authenticate successfully, the response body contains an HTML login page, indicated by an <html> tag. The API client must check the response body for the <html> tag to determine if authentication was successful.
Get XSRF Token
Get an XSRF prevention token, necessary for most POST operations:
GET /dataservice/client/token with content type application/json in the request header.
# Retrieve the JSESSIONID session hash from the cookie.text file from the earlier CURL example.
curl -X GET \
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/dataservice/client/token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Cookie: JSESSIONID=<session hash>"
GET https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address>/dataservice/client/token
HTTP Request Header:
{'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Cookie': 'JESSIONID=<session hash>'}
The response body includes the XSRF token, as shown in the following example:
HTTP Response Body:
'<String containing the XSRF token>'
Make an API Request
HTTP GET requests perform idempotent operations, meaning running them multiple times does not change anything in Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. Typically, HTTP request headers for these requests do not include an XSRF token. Therefore, for GET requests, the user must only include the JSESSIONID as a cookie within the request header.
curl -X GET \
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/dataservice/device" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Cookie: JSESSIONID=<session hash>"
GET https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address>/dataservice/<some API endpoint URL>
HTTP Request Header:
{'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Cookie': 'JESSIONID=<session hash>'}
HTTP POST requests often not idempotent. They can include form data which can result in changes to the Catalyst SD-WAN Manager. As such, they typically do require an XSRF token in addition to the JSESSIONID cookie within the HTTP request header.
curl -X POST
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/dataservice/<some API endpoint>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-H "Cookie: JSESSIONID="
-H "X-XSRF-TOKEN: "
-d "{}"
POST https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address>/dataservice/<some endpoint>
HTTP Request Header:
{'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Cookie': 'JESSIONID=<session hash>', 'X-XSRF-TOKEN': '<XSRF token>'}
Note: For HTTP GET requests, including the XSRF token in the header is optional; the system ignores it if not needed.
Log out of SD-WAN Manager and Destroy the Session
With the session-based (JSESSIONID) authentication method, log out after completing requests to all necessary API endpoints. It is not only a good security practice but also a way to release the allocated session resource.
POST /logout with the optional nocache=<random number> query parameter that makes the request unique. Submit the JSESSIONID cookie within the HTTP request header.
To log out of SD-WAN Manager, use the following code:
curl -X POST \
"https://<SD-WAN Manager IP address:port>/logout" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Cookie: JSESSIONID=<session hash>"
Sample Code to Authenticate with Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager
The following code example illustrates the use of session-based authentication:
class Authentication:
@staticmethod
def get_jsessionid(vmanage_host, vmanage_port, username, password):
api = "/j_security_check"
base_url = "https://%s:%s"%(vmanage_host, vmanage_port)
url = base_url + api
payload = {'j_username' : username, 'j_password' : password}
response = requests.post(url=url, data=payload, verify=False)
try:
cookies = response.headers["Set-Cookie"]
jsessionid = cookies.split(";")
return(jsessionid[0])
except:
print("No valid JSESSION ID returned\n")
exit()
@staticmethod
def get_token(vmanage_host, vmanage_port, jsessionid):
headers = {'Cookie': jsessionid}
base_url = "https://%s:%s"%(vmanage_host, vmanage_port)
api = "/dataservice/client/token"
url = base_url + api
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers, verify=False)
if response.status_code == 200:
return(response.text)
else:
return None
Auth = Authentication()
jsessionid = Auth.get_jsessionid(vmanage_host,vmanage_port,vmanage_username,vmanage_password)
token = Auth.get_token(vmanage_host,vmanage_port,jsessionid)
if token is not None:
header = {'Content-Type': "application/json",'Cookie': jsessionid, 'X-XSRF-TOKEN': token}
else:
header = {'Content-Type': "application/json",'Cookie': jsessionid}
Note: API requests header for GET/POST/PUT/DELETE are:
- For Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager pre 19.2 - Session Cookie (jsessionid)
- For Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager post-19.2 - Session Cookie (jsessionid) and Token
Sharing the same session is mandatory when invoking multiple API requests sequentially. The lifespan of a default session is 24 hours, and the session inactivity timeout is 30 minutes.
The maximum concurrent session number is 100. The system invalidates the least recently used session when the maximum number of concurrent sessions is reached by starting a new session.
Refresh Expired Tokens
The session token (JSESSIONID) for Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager expires after 30 minutes of inactivity or after 24 hours, which is the total lifespan of a session. For more information, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/sdwan-xe-gs-book/cisco-sd-wan-API-cross-site-request-forgery-prevention.html
The cross-site request forgery prevention token (X-XSRF-TOKEN) remains valid for the duration of the session and belongs in the header of each API request. For more information, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/sdwan-xe-gs-book/cisco-sd-wan-api-cross-site-request-forgery-prevention.html
SSO Authentication in Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager
If you enable SSO authentication on Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager, you can copy the JSESSIONID and X-XSRF-Token from your browser to authenticate an API request.
- Log in to Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager with SSO in your browser.
- From your browser's developer tool, select "Network"*.
- Inspect an API request.
- From the API request headers, copy the value of
Cookie: JSESSIONID=<session hash id> and X-XSRF-TOKEN: <XSRF token>. - Use the JSESSIONID and X-XSRF-TOKEN for API authentication.