Authentication
The Services APIs are REST-based, sending HTTP GET and POST requests to the Services APIs cloud, authenticating each request by providing an HTTP Authentication header and Bearer access token.
For example:
GET /cs/api/v1/customer-info/customer-details HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer S0w9Dqsjalskdjfa908uasdf890NW21S8
Accept: application/json
Host: apix.cisco.com
To obtain this API access token, the application must first make a request to the Cisco Common Identity SSO endpoint at https://id.cisco.com/oauth2/default/v1/token, providing a Client ID/Client Secret associated with the application instance. This set of credentials uniquely identifies the application and its access/roles/permissions with regard to accessing customer service data.
Note: To obtain a Client ID/Client Secret pair, see the Application Registration
Access-token generation
The access token authentication request is based on the OAuth2 client credentials grant flow, which is a single request/response transaction not requiring any user interaction to complete.
The following details define the authentication HTTP request:
- HTTP method:
POST - URL endpoint:
https://id.cisco.com/oauth2/default/v1/token - Content-Type:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded - Body: URL-encoded parameters:
- grant_type:
client_credentials - client_id: (your application Client ID)
- client_secret: (your application Client Secret)
- grant_type:
The raw request will look something like:
POST /oauth2/default/v1/token
Host: id.cisco.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 119
grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=b441B255redacted09fc5b&client_secret=b441Bredactedaf5b75d886b429
The response, as shown below, includes an access_token field, as well as an expires_in field representing the number of seconds indicating access token is valid for one hour.
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
"access_token": "eyJraWQiOiI4YlZLWHBnMjlLNUl4Wnh2TE9LejBQOTFBYV9GRVUxNHV2LTF5SERncDJVIiwiYWxnIjoiUlMyNTYifQ.eyJ2ZXIiOjEsImp0aSI6IkFULmlEd1VUYkZSaVRLTEx0aUQ4Tm4wdkUzU3ZPNkY3RVZVVzhzLWxodWYyN3MiLCJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL2lkLmNpc2NvLmNvbS9vYXV0aDIvZGVmYXVsdCIsImF1ZCI6ImFwaTovL2RlZmF1bHQiLCJpYXQiOjE3MDEyNjQ5MDcsImV4cCI6MTcwMTI2ODUwNywiY2lkIjoibTlmZmpwZzdoNm1tNnZ0a21wdm5kNmhtIiwic2NwIjpbImN1c3RvbXNjb3BlIl0sImFjY2Vzc19sZXZlbCI6MSwic3ViIjoibTlmZmpwZzdoNm1tNnZ0a21wdm5kNmhtIiwiZnVsbF9uYW1lIjoibnVsbCBudWxsIiwiYXpwIjoibTlmZmpwZzdoNm1tNnZ0a21wdm5kNmhtIn0.QcexN7PowxVMgvYHMCyA4jp9zwbKfaovmMF8vB6G86d10a4APnkhksF4m8mU-k33CFOS0nBTy2Z9dEQbaDR0IA0OI9k9_3KW0BUQSqzazEddJCbUOKQTVMNe-L5uN8jINHcJrki9v8YzxKuxdnBgasBhTiLZz5zJ4M9-pOIFS03bG6ICDxEM94OMOAd_loT5YlZfuPFz77S0-Tin8aICONCoydUftlLik24KUhrtT8M2TyqG9Gsvrfn8ClQsn-pXJvvx4JZvsSoZWR1UtqkQpzx7SwYLje30MnhDfbBkqn528F_LLmLQiqBBpmEVcu0-9VfZaEq7MwMGvGWfAmRkRg",
"scope": "customscope"
}
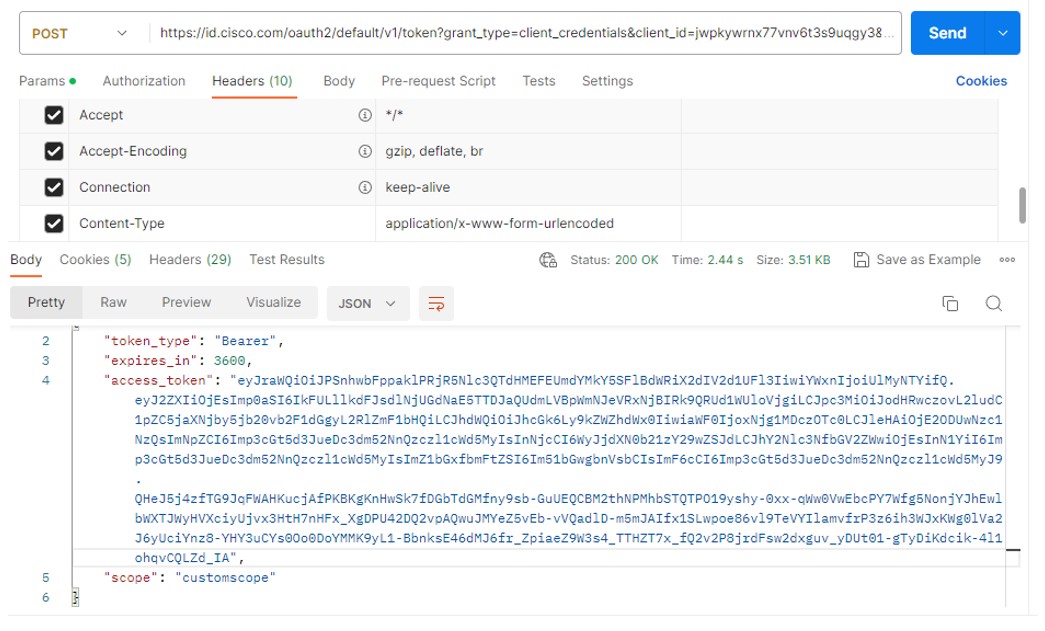
a. Example code snippet for Postman:
https://id.cisco.com/oauth2/default/v1/token?grant_type=client_credentials
&client_id=XXXXXXXXXXXXX&client_secret=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded to be passed as part of headers while making a token call.
b. Example code snippet for CURL:
--location --request POST 'https://id.cisco.com/oauth2/default/v1/token'
-d 'grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=XXXXXXXXXXX&client_secret=XXXXXXXXXXXX
-- header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
Once the access token has been generated, it must be provided when invoking each API request, as part of the Authentication header.
Note: The default lifetime for a client credential access token is 3600 seconds (1 hour) as of this writing. After the expiration time (or at any time prior), the application can acquire a new access token by repeating the authorization process above.