Introduction
Cisco DNA Spaces is now Cisco Spaces. We are in the process of updating our documentation with the new name. This includes updating GUIs and the corresponding procedures, screenshots, and URLs. For the duration of this activity, you might see occurrences of both Cisco DNA Spaces and Cisco Spaces. We take this opportunity to thank you for your continued support.
Cisco Spaces Software Development Kit (SDK) is a tool created and maintained by Cisco which leverages OpenRoaming technology to attach users, seamlessly and securely, to Wi-Fi networks without the need for user interaction. OpenRoaming leverages an Identity Federation, so that users can be attached to Wi-Fi networks based on a verified identity. This identity is used in user analytics and engagement. The Cisco Spaces SDK allows an iOS or Android application developer to configure iOS and Android devices with an identity of choice that can be verified with the back-end system. The Cisco Spaces SDK further allows the developer to add more information about the users, and engage with them, directly on their device, through the iOS and Android notification framework.
Use cases
Some of the use cases that are enabled by the Cisco Spaces SDK are listed below:
Create a differentiated experience for loyal customers with seamless and secure Wi-Fi onboarding
Guest wireless onboarding is still a pain point today: When a good LTE connection is available, users often do not bother to go through the manual experience of finding the right SSID and going though multi-steps onboarding. Often, users also have security concerns with the open Wi-Fi networks. These concerns have led to low adoption in many public Wi-Fi networks.
With the Cisco Spaces SDK, loyalty app users can seamlessly and securely connect to Wi-Fi without manually selecting a specific SSID. This automatic connection provides the venue staff with the customer's arrival information. Based on the customer loyalty levels, you can design and provide differentiated engagements and customer experiences.
Apart from loyalty customers, you can use this functionality for all your app customers, for example: customers having fan apps, enterprise apps, support apps, etc. and leveraging any of the supported identity types.
Drive contextual and location based targeted engagement and marketing campaign
Combining the SDK and other applications in Cisco Spaces, you can integrate identity and location data to create targeted engagements by pushing timely notifications and driving more marketing campaigns. For example: You can promote credit cards through the app.
When leveraging the Cisco Spaces SDK and provisioning an OpenRoaming identity, Cisco Spaces engage engine can use this identity to engage with the user, creating identity-based personas, and using location triggers to engage by leveraging the iOS and Android notification framework, thereby delivering notifications directly to the device.
Drive up loyalty app downloads and in-store app usage
With differentiated experiences offered by the loyalty app, customers will be more incentivized to download the app and sign up to become the loyalty member. Furthermore, with automatic in-store Wi-Fi connection, it’s expected that customers will use the app more often. This could enable the venues to design more in-store services based on the app. As a result of increased app usage, customers’ brand stickiness will be increased as well.
Address privacy MAC challenges
With the Cisco Spaces SDK, we will identify devices and users based on the loyalty ID associated with the loyalty profile, instead of the device MAC ID. This helps eliminate any potential impacts brought by the upcoming MAC randomization policies from iOS, Android, and Microsoft.
About OpenRoaming
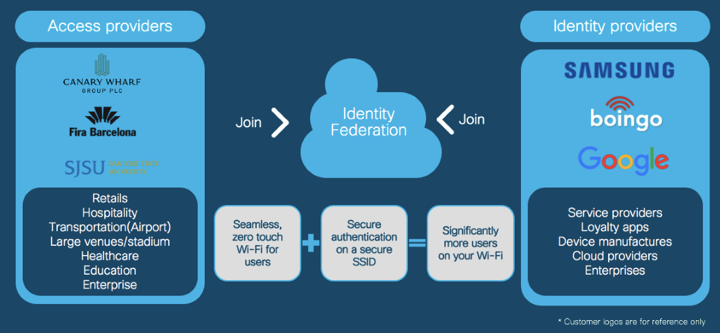
OpenRoaming has become a WBA (Wireless Broadband Association) industry standard. It is built around a consortium of Identity Providers (namely, the device manufacturers such as Samsung, Service providers, Cloud/Social providers, including Google and Facebook, and Enterprises) and Access Providers (large enterprises, retail stores, public venues, etc.) that will allow for easy roaming and a no-touch, seamless onboarding, wherever trusted users arrive. For example: Grab a cup of coffee from Starbucks, head over to Kohl’s to do some shopping, and catch a game at AT&T Park and be connected to each location's guest Wi-Fi, seamlessly. Imagine this happening across any B2C venue that joins this consortium. The goal is to give B2C venues their data ownership back, simplify guest access, and encourage people to use more Wi-Fi. It’s an opportunity for the consortium and its members to move the market for more Wi-Fi adoption, provide value to end users, and be thought leaders in the industry.
Figure 1: OpenRoaming Identity Federation
Provisioning devices of OpenRoaming users
An OpenRoaming user profile should be provisioned in a user's mobile device beforehand to enable automatic on-boarding to a Wi-Fi network associated with an OpenRoaming Federation. Typically, the Identity Provider should handle this provisioning.
There are 3 types of Identity providers that can join OpenRoaming:
- Cloud Identity providers, such as Samsung ID, Google ID, Apple ID, Facebook ID, etc
- Service Providers
- Enterprises and Loyalty programs
Figure 2: OpenRoaming IDPs
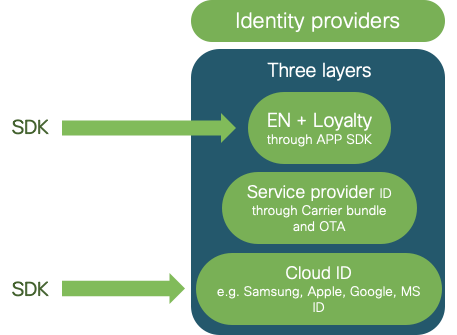
Service providers will provision mobile devices through a carrier bundle that is available on mobile devices or through Over-the-Air (OTA) provisioning interfaces.
For the other categories, Cloud IDPs, and Enterprise/Loyalty, the primary methods for provisioning devices and managing user profiles for OpenRoaming will be through the App integration.
In order to facilitate integration into apps, for example: loyalty apps or enterprise apps, the Cisco Spaces Android SDK and the iOS SDK facilitates provisioning devices and managing user profiles for OpenRoaming.