Most applications expose some sort of API that governs how an application can be accessed by other applications. APIs provide a set of routines, protocols, tools and documentation which can be leveraged for programmatic interaction. They represent a means through which elements or applications can be programmatically controlled and describe how external applications can gain access to capabilities and functions within another application. APIs have four primary components:
- Methods: Describes the mechanism of the API implementation including how resources communicate and provide encapsulation.
- Actions: This is the intent of the API call, often referred to as a "verb". It describes the operations available such as GET, PUT, POST, and DELETE
- Objects: This is the resource the user is trying to access. This is often referred to as a noun and it is typically a URI.
- Formats: This is how the data is represented, such as, JSON and XML.
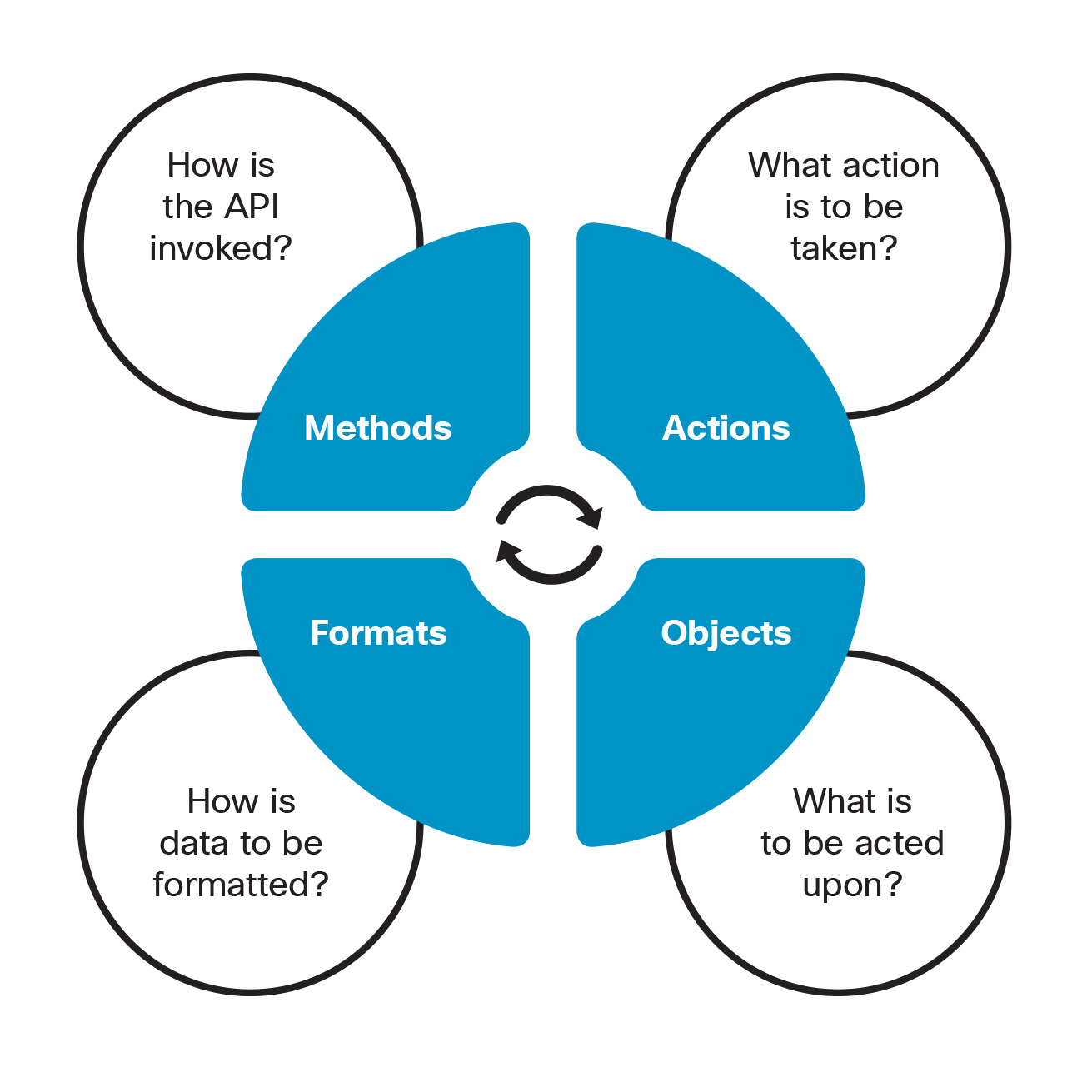
API Framework
The following characteristics of an API enable users to build a more efficient, manageable and reliable network via automation.
- Modularity: Applications can be built leveraging clearly defined and reusable modules
- Abstraction: APIs abstract the details of the underlying implementation from the higher level logic that invokes it
- Stability: APIs provide a stable and consistent interface
Cisco Open NX-OS exposes three primary APIs:
- NX-API REST - HTTP-based RESTful API
- NX-API CLI - RPC-based API
- NETCONF API
Each of these APIs can be used with multiple language bindings. There are Python bindings for both NX-API REST and NX-API CLI.
This chapter will explore the Open NX-OS RESTful APIs in more detail.