Cisco GPT overview
Use Cisco Gateway Provisioning Tool (GPT) to build a supported gateway for use with Cisco GMM. This tool provisions the Cisco router to be managed by Cisco Gateway Management Module (GMM) by installing the required IOS and IOx firmware and base configurations.
This may be necessary if:
- You need to convert an existing router for use with Cisco GMM
- You want to restore your router to the default state for use with Cisco GMM
- You receive a replacement RMA device
Notes:
- Provisioning will re-image the gateway with a Cisco IOS version that may be different that the currently installed version. In addition, any saved configurations will be lost and a new configuration will be added when the device is claimed in Cisco GMM. Be sure you understand what Cisco Gateway Management features are supported before provisioning a gateway. If provisioning a customer's gateway, always get their consent and explain the impact of provisioning on the device.
- You can also convert a GMM gateway back to a standard Cisco gateway.
- RMA GMM gateways are standard Cisco gateways.
- Always exit your serial application when running GPT to avoid serial port conflicts.
- For additional details, click here.
About this release
See the GPT Release Notes for information about new and revised features, including open and resolved issues.
Requirements
| Requirement | More information |
|---|---|
| Mac, Windows, or Linux host computer | Cisco GPT is currently supported on the MacOS, Windows, and Linux platforms. |
| No VPN on host computer | The host computer should not be connected to any VPN profile. Otherwise, the GPT tool will not communicate with the Gateway. |
| Complete the prerequisites | Before you begin, complete the prerequisites for your Mac, Windows, or Linux host computer. |
| Ethernet cable | Connect an Ethernet cable from the IR8x9 gateway to the host machine. |
| A mini-USB to USB cable | Connect the cable from the gateway's mini-USB port to the computer's USB port. |
| Install the USB drivers | Download and install the USB drivers on your computer, if necessary. |
| Static gateway IP addresses and subnet | The IP address and subnet are used to establish communication between the gateway and host computer. For example, you can use: |
| host computer—192.168.3.2 | |
| gateway—192.168.3.3 | |
| subnet on both devices—255.255.255.0 | |
| Cisco GMM GPT | Download and install the GPT provisioning app on your host computer. |
Prerequisites
Before you begin, complete the following tasks for your Gateways.
Also complete the prerequisites for the Mac, Windows, or Linux host computer you will use to perform the provisioning.
Verify the Python version
GPT requires Python 2.7, which it will install. To avoid conflicts, you may need to remove other Python versions and ensure that the path is correctly set for GPT.
In the following example, version 3.6.5 is installed and may conflict with the GPT version. Remove this version before using GPT.
unix$ python
Python 3.6.5 |Anaconda, Inc.| (default, Apr 26 2018, 08:42:37)
[GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Clang 4.0.1 (tags/RELEASE_401/final)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.In the following example, the correct Python 2.7 is installed:
unix:~ demo$ python
Python 2.7.10 (default, Oct 6 2017, 22:29:07)
[GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 9.0.0 (clang-900.0.31)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.Verify the serial connection
Verify that the serial connection from your laptop to the gateway is working, and that the correct drivers are installed.
You can verify this by successfully connecting to the gateway's serial port using a serial application.
Note: Stop all serial applications before running GPT or a serial port conflict may occur.
Gateway prerequisites
- The gateway must have 500MB of flash storage available. The GPT will optionally remove files, or you can manually remove files.
- The gateway must not have a password, or must already be provisioned as a GMM Gateway with the default GMM password (unclaimed gateway).
- Factory reset the gateway to delete the existing password and configuration.
- If using an IR829 gateway, the AP must be in autonomous mode and not unified mode. If AP is in unified mode, convert AP to autonomous mode.
Mac prerequisites
Complete the above Requirements.
Linux prerequisites
Install gksu using sudo apt-get install gksu command.
Copy the installer to any location on the host computer.
Change the permission of the installer to 755.
Run the installer using sudo.
sudo ./ GPT-setup
Follow the onscreen prompts to complete the installation.
Note: Do not change installation directory
/usr/local/GPT.Open the application and enter the root password when prompted.
The application should launch and detect the attached gateway.
Windows prerequisites
GPT supports Windows 7 and Windows 10 only.
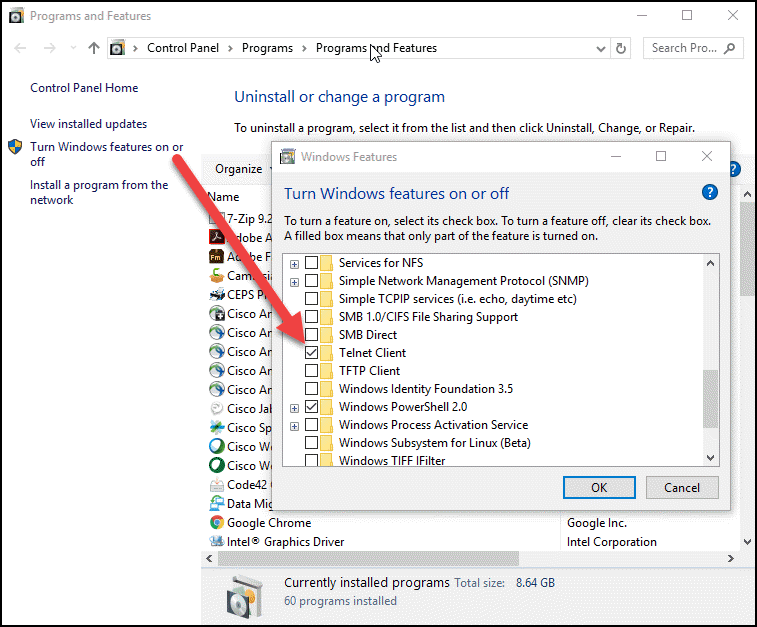
Before you begin, enable telnet on your windows computer:
- Click Start and search for "appwiz.cpl" (or go to Start > Control Panel > Programs and Features).
- On the left side panel, click Turn Windows feature on or off.
- Select the Telnet Client box and click OK.
- Reboot the system if prompted.
- Install the GPT tool on your Windows machine using the setup file provided separately.
Provisioning Steps
Complete the Requirements.
Complete the Prerequisites.
(Mac and Windows) Download and install the provisioning app.
- Download the provisioning tool to your computer. Contact your Cisco Partner for assistance, if necessary (find a Cisco Partner).
- Double-click the downloaded file and click OK to launch the tool.
- Follow the onscreen prompts to install the software.
Ensure the gateway does not have a password by resetting the device. This erases the configuration and allows the provisioning tool to discover the device.
Connect your host computer to the gateway.
Connect an mini-USB cable from the gateway console port to the computer USB port.
Connect an Ethernet cable from the gateway to your computer.
Specify the gateway port you are connected to in the GPT tool.
Configure a network connection between your host computer and the gateway.
This connection is used to copy the firmware images to the IR8x9. You can use any IP address and subnet.
- For example, on your Mac, select the WiFi icon and Open Network Preferences.
- Select the Ethernet port that is connected to the gateway.
- Configure IPv4—Enter Manually.
- IP address—Enter a host computer IP address. For example 192.168.3.2.
- Subnet Mask—Enter the subnet. For example 255.255.255.0.
- Click Apply.
Run the GPT provisioning app and select the gateway.
- Verify the serial connection between you computer and the gateway.
- Open the GPT app on your host computer.
- (Optional) Click ? in the title bar to view the GPT tool version, AGP version and required license for your OS.
- Wait for the app to scan for devices connected to the computer over the USB-mini USB cable.
- If your gateway does not appear, click Rescan to discover devices again.
- If "No Gateway detected" appears, click Troubleshoot and then Export Log to generate and save a log that can be sent to Cisco support for analysis and troubleshooting. The log helps Cisco support identify issues such as firewall settings, incorrect environmental variables, missing libraries, or other issues that can prevent the gateway from being discovered.
- Select your gateway.
- (Optional) Click Details for information about the device, such as the part number, current IOS version, Hypervisor version, Guest OS (GOS) version, the host machine port where the device is connected, and the call-home URL (your organization's GMM cluster URL).
Click Provision.
In the Gateway tab, enter the following and click Next to apply the default router configuration.
Note: The default configuration allows applications to run on the gateway.
- Call home URL—Enter the hostname or IP address of your Cisco GMM cluster. You can also select one of the default options if used by your organization.
- LAN Interface—Select the gateway interface that is connected to the host computer, such as GigabitEthernet1.
- Gateway IP—
- Click Dynamic If both the gateway and host computer are connected to switch with a DHCP server.
- Click Static to enter the network details manually.
- IP—Enter the device IP address used to copy the firmware images to the gateway. This should be in the same range as the IP address configured on your computer. For example, if the IP address on your computer is 10.0.0.2, enter a gateway IP address in the same range, such as 10.0.0.5.
- Subnet—Enter the same subnet used for the host computer.
- Click Next.
In the Host tab, enter the Host IP
This should be automatically entered based on your computer's IP address. If not, enter the host computer IP address that was entered in the computer network settings in Step 6.
(Optional) Click Advanced and select an alternative provisioning option:
- Provisioning without Cartridges—Select this option if the gateway will not run applications. Note: Cartridges are containers used to run applications on the gateway.
- Provisioning with User Configuration—Select this option and enter a custom set of IOS configuration commands to run on the router. For example, you can copy-and-paste standard configuration commands used by your organization.
- Click Start Provisioning.
Click Start Provisioning.
Click OK to confirm that provisioning can take 20-30 minutes. Do not power off the device during this time.
Click Yes or OK to confirm the software image versions and continue.
Note: If an "Insufficient memory" error occurs, log into the gateway IOS CLI using a terminal and delete images or other files that are consuming space. If this happens, start the provisioning again.
(Optional) Click the arrow next to the progress bar to display the detailed event log.
If an error occurs, click Export Log to export the information and provide it to your Cisco support representative.
Click OK when the provisioning process is complete.
(Optional) Revise the optional settings
Click Settings to change the APN name, enter a static IP address, or upgrade the cellular modem firmware.
Change the APN name for your gateway
- Complete the provisioning steps using the default settings.
- Run the GPT tool again.
- Select the gateway.
- Click Settings and select the Cellular tab.
- Enter the APN name.
- For Dual LTE devices, select the Cellular 0 or Cellular 1 interface and enter the APN name.
- Click Apply to save your changes.
Enter a static IP address for the Ethernet WAN interface
- Complete the provisioning steps using the default settings.
- Run the GPT tool again.
- Select the gateway that requires a static IP address configuration.
- Click Settings and select the Ethernet tab.
- Enter the static IP address, subnet mask, default gateway IP and DNS IP addresses for the gateway.
- Click Apply to save your changes.
Notes
- Use this if a DHCP server is not used to provide the IP configuration.
- These fields are populated if a static IP configuration is already configured on the device.
- Site-to-site VPN and Workgroup bridge (WGB) do not work if a static IP configuration is used. These features require DHCP.
Upgrade the cellular modem carrier and firmware
- Complete the provisioning steps using the default settings.
- Run the GPT tool again.
- Select the gateway.
- Click Settings and select the Cellular Modem tab.
- Enter the Host IP, which is the IP address of the PC you are using for provisioning.
- Enter the LAN IP and subnet mask, which is the gateway's IP address.
- Next to Cellular Interface, select the SIM port.
- Next to Cellular Firmware, select the cellular carrier. The firmware will be upgraded for that carrier.
- Click Upgrade.
- Wait for the upgrade to complete. The cellular modem will restart during this process.
Troubleshooting
If provisioning fails, try the following troubleshooting steps.
If your gateway does not appear when you launch the GPT tool, click Rescan to discover devices again.
- If "No Gateway detected appears", click Troubleshoot and then Export Log to generate and save a log that can be sent to Cisco support for analysis and troubleshooting.
- The log helps Cisco support identify issues such as firewall settings, incorrect environmental variables, missing libraries, or other issues that can prevent the gateway from being discovered.
Factory reset the gateway to ensure the device has the default password. This allows the provisioning tool to discover the device. See the Provisioning steps for details.
Ensure that all prerequisites for your computer platform were successfully completed.
Make sure that you have sufficient privileges on the host computer to Install GPT.
For example, you must have administrative privilege to install GPT application on a Windows machine.
Connect your host computer to the gateway.
- Connect the mini-USB cable from the gateway console port to the computer USB port.
- Connect the Ethernet cable from the gateway to your computer. Be sure to select the same port in the GPT tool that the computer is physically attached to. For example:
- IR829: Connect the Gig1 port
- IR809: Connect the Gig0 port
Check serial connectivity with the host machine.
Install the serial–USB connector driver.
Install Putty.exe.
On a windows machine, open the Device Manager and verify that the COM port on which device is connected.
Open Putty.exe and connect to the device as a serial device using above COM port.
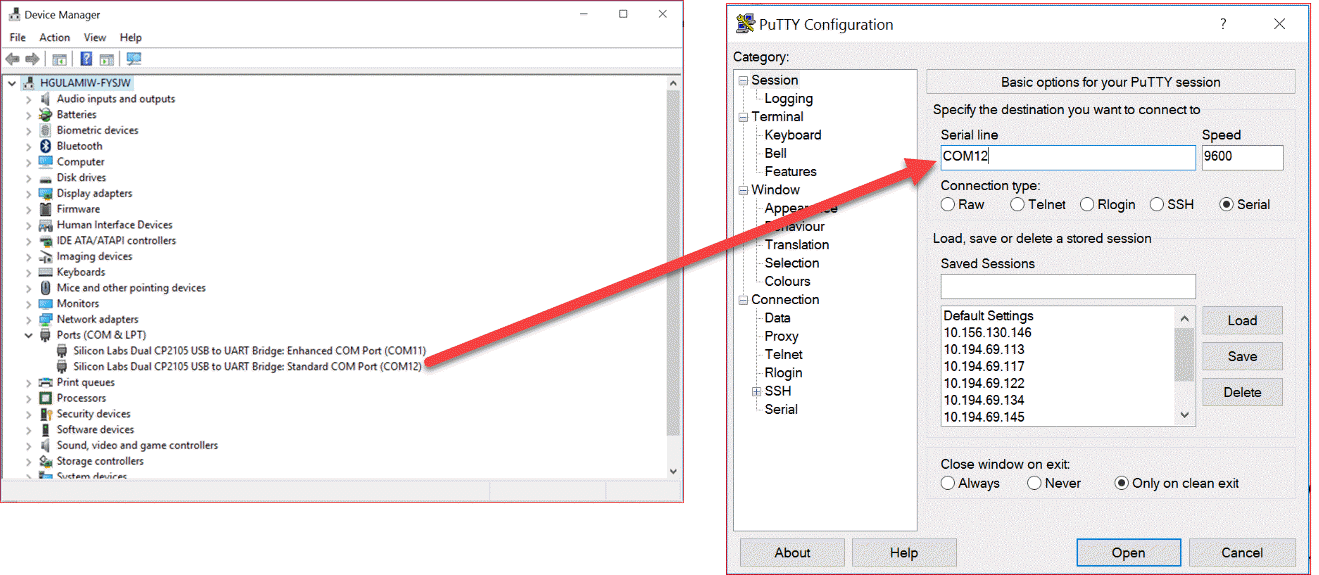
Try to login using default gateway username and password.
Disconnect the device.
Ensure that the device serial console is not connected using any other application (such as Putty, Minicom, Teraterm, etc.).
Ensure that the host machine's firewall or anti-virus software does not block the GPT application.
Make sure no other service is running on TCP port 8000/2217, which is used by GPT.
Configure the network connection between your host computer and gateway on the same subnet.
Ensure that the gateway has enough flash storage space to copy the images.
Only Python 2.7 is supported. Python 3.0 should not be installed.
GPT supports Windows 7 and Windows 10 only.
Next Steps
Provisioning returns the gateway to an out-of-box state. Complete the instructions in Deploy your gateway. For example:
- After provisioning, the gateway must be registered to your GMM account by a Cisco support representative.
- Log in to the Cisco GMM Cloud Application.
- Click Support to open a support case.
- Include the device model and serial number in your message.
- Click Send.
- Connect the gateway to the Internet.
- The cellular service can be used if supported on the device.
- An Ethernet cable can also be connected from the gateway to the Internet uplink port. Use Gig0 for IR809 and Gig1 for IR829 gateways.
- Deploy your gateway using the Cisco GMM Cloud Application.
- The device is available for use after it is registered by Cisco and claimed by someone in your organization.
More information
Revert a GMM gateway to a standard gateway
To convert a GMM gateway back to a standard Cisco gateway, enter the following commands:
- Factory reset the gateway to put the gateway into a clean GMM base state.
- Connect and log in to the gateway console.
Cisco Kinetic Gateway v1.91
User Access Verification
Username: admin
Password:
IR800#Delete or rename the GMM base configuration.
IR800#dir flash:*.cfg Directory of flash:/*.cfg Directory of flash:/ 27 -rw- 5612 Mar 30 2019 15:57:36 +00:00 base-IR800.cfg 994918400 bytes total (625852416 bytes free) IR800# delete flash:base-IR800.cfg or IR800# rename flash:base-IR800.cfg flash:base-IR800.saveErase the startup configuration.
IR800#erase startup-configReload the router. The router will boot up as a standard gateway.
IR800#reloadIf prompted to save configuration, answer
No.
NOTE: For the gateway to use the base-IR800.cfg file, the gateway must be factory reset. Learn more
Manually Removes Files
Determine which image is being used, and be sure not to delete that image.
For example, view the current image:
IIR829_FTX19438012#sho ver | inc image
System image file is "flash:/ir800-universalk9-mz.SPA.158-3.M0a.default"
IR829_FTX19438012#sh platform hyper
version: 3.0.60And be sure not to delete that image:
IR829_FTX19438012#dir flash:
13 -rw- 25196913 Mar 13 2019 02:03:34 +00:00 ir800-hv.srp.SPA.3.0.60.default
26 -rw- 64490930 Mar 13 2019 02:05:12 +00:00 ir800-universalk9-mz.SPA.158-3.M0a.defaultNext, delete the unused IOS, IOX and hypervisor images:
For example:
IR829_FTX19438012#delete flash:ir800-universalk9-mz.SPA.155-3.MDelete files in flash:/managed directory. For example:
IR829_FTX19438012#delete /force /recursive flash:/manageCheck that there is adequate space in the flash:
IR829_FTX19438012#dir
994918400 bytes total (716931072 bytes free)Convert AP To Autonomous Mode
To check that your AP is in Unified mode, session over to the AP, which will show the AP prompt.
ap>Unified Mode shows the AP's MAC address (based on the BVI interface):
AP6cb2.aea5.21ca> If the AP is in Unified Mode, check the directory to see if an Autonomous AP image exists, and then boot that image.
Check the directory:
ap: dir flash:
Directory of flash:/
2 -rwx 5 <date> private-config
3 drwx 2048 <date> ap1g3-k9w7-mx.153-3.JC
208 drwx 2048 <date> ap1g3-k9w8-mx.153-3.JC
-k9w7- This is autonomous image
-k9w8- This is unified imageBoot the autonomous image, and the AP should boot in autonomous mode:
> boot flash:ap1g3-k9w7-mx.153-3.JC/ap1g3-k9w7-mx.153-3.JCDownloading a new image
If the autonomous image fails to boot (for example, due to a corrupt image), download a new image down to the AP.
To do this,
- Copy the image to the gateway.
- Make the gateway the TFTP server for the image.
- Install the image from the IR829 gateway.
Copy AP image to router:
Connect to the console of the AP from the gateway.
Note: Add an IP address if the wlan-ap 0 interface does not yet have one.
# conf term
IR829(config)#interface wlan-ap 0
IR829(config-if)# no shut
IR829(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
IR829(config)#interface Wlan-GigabitEthernet0
IR829(config)# switchport mode access
IR829(config-if)# end
IR829# service-module wlan-ap 0 session
Trying 1.1.1.1, 2004 ... Open
User Access Verification
Username: cisco
Password: Cisco
ap>ena
Password: CiscoIf the AP is in Unified mode, set AP to local mode to stop it from rebooting.
ap# capwap ap mode local
If necessary enable debug mode
ap# debug capwap console cli
Ensure AP has IP address on BVI interface.
ap(config)# int BVI
ap(config)# ip address dhcp
Verify that AP has IP address
# show ip interface briefTo connect back to the gateway, type CTRL-SHIFT-^, then X
Copy necessary AP code to the gateway flash. Use a current AP 803 image.
Example: ap1g3-k9w7-tar.153-3.JI1
copy tftp: flash:
copy ftp: flash:or enable scp
# conf term
IR829(config)# ip scp server enable
copy scp: flash:Configure the IR829 to be tftp server for the image.
On the IR829gateway:
ir829 (config) # tftp-server flash:”ap_image_name”On the AP:
# archive tar /xtract tftp://<ip of gateway> tar flash:Note: Subsitute ip of gateway with the gateway IP address.