IOSv
Overview
IOSv is an implementation of Cisco IOS that runs as a full virtual machine. The IOSv images are built from the Cisco IOS M/T train and support up to 16 GigabitEthernet interfaces. IOSv provides full layer-3 control-plane and data-plane functionality. Layer-2 switching is not supported, but layer-2 encapsulations, such as EoMPLS and L2TPv3, are supported.
Limitations
IOSv is performance limited when forwarding traffic. Achieved throughputs are ~2.8 Mb/s when passing traffic through one IOSv router, and ~2.4 Mb/s when chained over two routers. Baseline throughput bypassing the router was ~720 Mb/s.
Forwarding performance has been tested with iperf running a basic test.
IOSv Features
Supported Features
The following features are included in the IOSv image:
- 802.1Q
- AAA
- ACL
- BGP
- DHCP
- DNS
- EEM
- EIGRP
- EoMPLS
- Flex Netflow + TNF
- GRE
- ICMP
- IGMP
- IP SLA
- IPSec
- IPv6
- ISIS
- L2TPv3
- MPLS
- MPLS L2VPN
- MPLS L3VPN
- MPLS TE
- Multicast
- NAT
- NTP
- OSPF
- PfR
- PIM
- PPPoE
- RADIUS
- RIP
- SNMP
- SSH
- SYSLOG
- TACACS
- TFTP
- VRF-LITE
Features that May Work
The following features have not been tested and are not officially supported, but they may work in the IOSv image:
- HSRP
- VRRP
- GLBP
- EZVPN
- QoS
- LISP
- ZBFW
- Performance Monitor
Unsupported Features
The following features are not supported by IOSv and are known not to work:
- OTV
- BFD
- VPLS
- Voice
- AVC
Features Tested with CML
Each CML release is tested with the bundled version of IOSv. The tests validate the following features:
| Test Name | Result |
|---|---|
| CDP | Pass |
| ping | Pass |
| OSPF single-area | Pass |
| NAT - static | Pass |
| HSRP | Pass |
| DHCP | Pass |
| Routed subinterface | Pass |
The lab used for the tests is IOSv Feature Tests, which is one of the sample labs included with CML on the Tools > Sample Labs page.
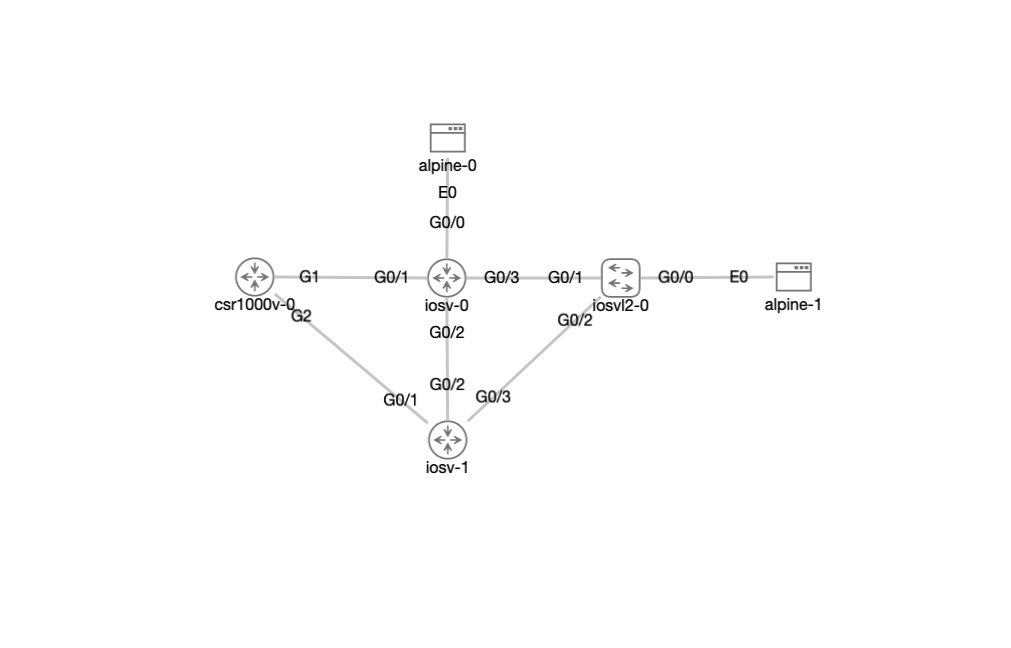
CDP
- peer device is detected on the interface and listed in the CDP table.
- Neighbor types: IOSv, IOSvL2, CSR1000V
Ping test
- Sending ICMP Echo packets to the neighbor IP
- Direct reachability and reachability via routing
OSPF Single-Area
- loopback interfaces configured
- point-to-point networks configured on links between routers
- all interfaces in area 0
- OSPF establishes connectivity
- Can ping loopback interfaces on different routers
NAT: Static
- Alpine Linux VM connected to the router, configured static IP on VM and on router interface
- static translation configured on a router
- loopback interface with the translated network configured, and included in OSPF
- ping of the untranslated VM IP from the router
- ping of the translated VM IP from a different router
HSRP
- two IOSv router, interconnected by a IOSvL2 switch
- Alpine VM connected to the switch
- HSRP configured on the two routers
- Ping between: VM IP to HSRP IP
- Verification: ping between: VM IP to SVI IP; SVI IP to HSRP IP; VM and SVI IP to interface IP
DHCP
- DHCP pool configured on a router
- Alpine Linux VM connected through the IOSvL2 switch
Routed subinterface
- created routed subinterface on two IOSv routers
- Interconnected them over the IOSvL2 switch; configured interfaces as trunks; configured VLANs on IOSvL2
- Configured an IP on the SVI for that VLAN on IOSvL2