Asset Types
Alert: Cisco has made the end-of-life (EOL) announcement for the Cisco Edge Intelligence.
An Asset Type is a template that defines the technical characteristics for assets of the same kind, including attributes and transport protocols. These asset types can be used later for configuring a concrete asset instance in EI. EI asset instance corresponds to a concrete sensor/PLC/controller/machine and contains all the necessary information to connect and retrieve data from this sensor/PLC/controller/machine. Each instance of an asset type created using such a template will be instantiated with the same characteristics, such as the number and name of attributes, attribute data types, industrial legacy protocol to be used, etc. This prevents post-processing to homogenize the data structure when adding assets of the same type.
Asset Types are also used in Data Logic scripts as the input source.
About Asset Type Model Definitions
While creating an Asset Type data model with static attributes, download the model JSON file after saving the model definition, which will then contain the static attributes.
Asset Types can have pre-defined (static) attributes and user-defined (dynamic) attributes. Both of these can be accessed in Data Logic scripts.
For data rule policies, the static attributes can be filtered out in the source filter similar to dynamic attributes. Learn more about data rules and data logic policies.
Asset Management Workflow
- Add an Asset Type.
- Create a Data Model.
- Test and verify the Data Model.
- Save the Asset Type.
- Add Assets by providing asset details and adding values for custom attributes.
- Map the asset to the associated EI Agent.
Adding Asset Types
- In the left menu, click Assets > Asset Types.
- In the right pane, click Add Asset Type.
- In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Type Name | The name for the asset type. Restrictions: * Do not use special characters in an asset name, it can cause an error, because special characters may get removed for internal processing. (For example, "The given asset type name conflicts with an existing asset type name "XYZ". Please choose a different name"). Recommended practice is to use camelcase, Eg: Please use waterSensorSalinityJ2345, coldStoragePlcV2 etc. instead of "Water Sensor-Salinity_J2345" or "Cold Storage Plc_V2 ". * Avoid ending an asset type name with the letter "s" to indicate plural form. This can cause internal naming conflicts. Eg: Please use "coldStoragePlc" instead of "coldStoragePlcs" |
| Connection Type drop-down | One of the following protocols can be used for asset connection: * MQTT * OPC UA * Modbus – TCP/IP * Modbus – Serial * Serial * NTCIP1202 * NTCIP1203 * NTCIP1204 * RSU * EIP/CIP |
After the selection of a Connection Type, follow the below given steps and complete the configuration of an asset:
- Define the connection configuration
- Based on the Connection Type, go to the relevant section in the document to understand the configuration parameters for that Connection Type.
- Define the data model
- The data model defines the list of attributes associated with a given type of assets. The attributes are classified into two categories:
- Attributes that the asset exposes using the appropriate protocol (based on the Connection Type).
- Custom attributes are attributes that are assigned to an asset as part of the asset definition in the EI cloud and are independent of the Connection Type.
- The data model defines the list of attributes associated with a given type of assets. The attributes are classified into two categories:
The data model can be defined in the EI GUI or can be specified in a JSON file and uploaded as part of asset type creation/updation. For each Connection Type, you can download the sample data model template with appropriate parameters from the portal.
Defining the data Model
Attribute Definitions - common fields
- Attribute Name — This corresponds to the logical attribute name inside EI on the asset type. For example, temperature.
- Label — This is visible inside the EI Cloud UI during Data Model Testing.
- Description — Add a more detailed and understandable description of the attribute. For example, measured approximately 20 centimetres above the ground in degrees Celsius.
- Data Type — This is the data type of the attribute.
The additional fields in the attributes will depend on the Connection Type.
Custom Attributes fields
- Attribute Name — This corresponds to the logical attribute name inside EI on the asset type. For example, temperature.
- Label — This is visible inside the EI Cloud UI during Data Model Testing.
- Data Type — This can be String, Double, File or Encrypted String.
- Field Validation — This is an optional field.
- Description — This is the place where you can add a longer human-readable description of the attribute. For example, In degree Celsius, measured approximately 20 cm above the ground.
- The constraints for defining or using an attribute of type File are given below:
- There can be only one attribute of type File for a given asset type.
- The max size of the uploaded file should be 12 KB.
- The file can be of any type - ASCII or binary.
- If the asset is part of a data rule policy and the destination is configured to send the custom attribute to the northbound destination, the base64 equivalent of the file contents will be sent.
- If the asset is part of a data logic policy, a custom attribute value will be available in the data logic script as a byte array (UInt8Array), and it can be converted to the original format for access.
- For example, if the custom attribute "reference_data" was of File type and the uploaded file was as ASCII file, the following code shows how to convert the value available as UInt8Array into ASCII text.
function on_update() { ... var file_contents = new TextDecoder().decode(input.reference_data); // Converts UInt8Array to ASCII ... }
| Serial Number | Input File Type | Output/Result | Snippets |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Text/JSON | String | var decoder = new TextDecoder () output.value = decoder. decode (input. FileAttr); output.publish() |
| 2 | JSON | JSON | publish("output",JSON.parse (decoder.decode (input.FileAttr))); |
| 3 | HEX | HEX | publish("output", decoder .decode (input.FileAttr)); |
| 4 | BIN | Base64 string | output.value = Duktape.enc ('base64', input.FileAttr); output.publish() |
Adding Asset Types for MQTT Connection Type
The MQTT asset type enables and configures the EI MQTT Server. You can publish data to the EI Agent from an MQTT client on the following ports after deploying this to an EI Agent:
- Port 8883 for TLS configurations
- Port 1883 for non-TLS configurations
Configure and use the Client ID from the Advanced Settings section on the Add Asset Type page in order to publish data.
Client ID, specified in the MQTT client connection, differentiates various MQTT connections to EI.
Note: The MQTT topic used to publish sensor data and the data format should match the data model JSON file.
MQTT data model example:
{
"apiVersion": 1.0,
"connectionType": "MQTT",
"fields": {
"temperature": {
"category": "TELEMETRY",
"label": "Temperature",
"description": "Outside temperature sensor XY | Temperature",
"datatype": "Float",
"topic": "sensors/tempXY/temp"
},
"humidity": {
"category": "TELEMETRY",
"label": "Humidity",
"description": "Outside temperature sensor XY | Humidity",
"datatype": "Float",
"topic": "sensors/tempXY/hum"
},
"attr1": {
"category": "ATTRIBUTE",
"label": "Attribute 1",
"datatype": "Float",
"description": "My Attribute 1",
"required": true,
"defaultValue": 12.9
},
"attr2": {
"category": "ATTRIBUTE",
"label": "Attribute 2",
"datatype": "String",
"description": "My Attribute 2",
"required": false,
"defaultValue": null
},
"encrypted_attr3": {
"category": "ATTRIBUTE",
"label": "New Attribute",
"datatype": "EncryptedString",
"description": "My Attribute 3",
"required": true,
"defaultValue": null
}
}
}
MQTT topic and sensor data used by MQTT Client example:
MQTT Client Topic: sensors/tempXY/hum
MQTT Client Data: 50.0
In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following additional fields.
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Details | |||
| Encryption | |||
| Enable TLS | Select the checkbox to enable TLS. After selection, upload Certificate and Private Key. The MQTT server, which will be deployed on the EI agent, will use these certificates and private keys to authenticate MQTT clients connecting to it. |
||
| Username | Enter the Username. The connecting MQTT Clients (sensors) will use this username for authentication at the MQTT Server which will be spawned on the EI Agent. | ||
| Password | Enter the Password. The connecting MQTT Clients (sensors) will use this password for authentication at the MQTT Server which will be spawned on the EI Agent. | ||
| Advanced Settings | |||
| Client Identification | Select Use Client ID. (Topic-based device/sensor identity detection is not yet supported). | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset and from which MQTT topics it should be updated. You can view and edit the Data Model using the EI interactive mode, or by uploading a JSON file. Select one of the following:
|
Adding Asset Types for OPC UA Connection Type
OPC UA data model example:
{
"apiVersion": 1,
"connectionType": "OPC_UA",
"fields": {
"temperature": {
"label": "Temperature",
"description": "",
"datatype": "Float",
"nodeId": {
"namespaceUri": "2",
"identifier": "2",
"type": "numeric"
},
"samplingInterval": 1000,
"category": "TELEMETRY"
}
}
}
In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following additional fields.
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Details | |||
| IP Address or Host Name | Enter the IP address or hostname. | ||
| Port | Enter the port number. | ||
| Publishing Interval | This is the requested publishing frequency from the OPC-UA Server. This has to be greater than or equal to 1000ms. Note: The OPC-UA Servers Publishing frequency is independent of the metric-specific sample interval. In case the sampling interval (in the attribute table below) of an individual metric is smaller than the publishing interval, the OPC-UA server will queue up and send all the sampled values for a metric between the last publish and the current publish. |
||
| Advanced Settings | |||
| Authentication | This can be one of the following: * Anonymous: The OPC-UA client inside the EI Agent will not authenticate at the OPC-UA Server - use this if your OPC-UA server does not have authentication enabled for connecting clients. * Username & Password: If you choose this, then enter the username and password - the EI Agent will use this username and password to authenticate at the given OPC-UA Server. |
||
| Security Mode | Select None. (The OPC-UA Modes Sign and Sign and Encrypt are not yet implemented). | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset. You can view and edit the Data Model using the EI interactive mode, or by uploading a JSON file. Select one of the following:
|
Adding Asset Types for Modbus TCP/IP Connection Type
Modbus TCP/IP data model example:
{
"apiVersion": 1,
"connectionType": "MODBUS_TCP",
"fields": {
"desired_temp": {
"label": "Desired Temperature",
"datatype": "Int",
"description": "WO",
"rawType": "UINT16",
"type": "HOLDING",
"pollingInterval": 5000,
"offset": 5,
"category": "TELEMETRY",
"access": "Write"
},
"temp_to_display": {
"label": "Temperature to be displayed",
"datatype": "Int",
"description": "RW",
"rawType": "UINT16",
"type": "HOLDING",
"pollingInterval": 5000,
"offset": 100,
"category": "TELEMETRY",
"access": "ReadWrite"
},
"temp": {
"label": "Current Temperature",
"datatype": "Int",
"description": "RO",
"rawType": "UINT16",
"type": "HOLDING",
"pollingInterval": 5000,
"offset": 1,
"category": "TELEMETRY",
"access": "Read"
}
}
}
In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following additional fields.
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Details | |||
| IP Address or Host Name | Enter the IP address or hostname. | ||
| Port | Enter the port number. | ||
| Advanced Settings | |||
| Zero on Failed Poll | The value if there is no response from the asset. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Use Batch Polling | To request batch responses from the asset. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Contiguous Batch Request Only | To request contiguous batch responses from the asset. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Use Multiple Write Commands | Do not change the default value. | ||
| Timeout | The time set to receive the data before it is reset. You can modify or keep the default value of 500. | ||
| Retries | The number of times the server requests for retransmission of data. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Max Read Bit Count | The maximum number of bits that the server reads in one read request. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Max Read Register Count | The maximum number of registers that the server reads in one read request. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Max Write Register Count | The maximum number of registers that the server writes in one write request. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset. You can view and edit the Data Model using the EI interactive mode, or by uploading a JSON file. Select one of the following:
|
Adding Asset Types for Modbus Serial Connection Type
Modbus Serial data model example:
{
"apiVersion": 1,
"connectionType": "MODBUS_SERIAL",
"fields": {
"pressureInPascal": {
"label": "MetrLabeModb1",
"pollingInterval": 50,
"offset": 12,
"type": "HOLDING",
"datatype": "Float",
"rawType": "VARCHARSTRING",
"description": "",
"access": "Write"
},
"TemperatureInDegrees": {
"label": "Temperature",
"pollingInterval": 41,
"offset": 56,
"type": "DISCRETE",
"datatype": "String",
"rawType": "INT16",
"description": "",
"access": "ReadWrite"
},
"HumidityInDegrees": {
"label": "Humidity",
"pollingInterval": 20,
"offset": 45,
"type": "COIL",
"datatype": "Int",
"rawType": "FLOAT64",
"description": "Humidity Value ",
"access": "Read"
}
}
}
In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following additional fields.
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Details | |||
| Transport | This field has a default value set to RTU. | ||
| Serial Port | Enter the port number. For example, /dev/ttyS0 | ||
| Serial Port Characteristics | |||
| Baud Rate | Search or add a value for the Baud Rate. By default, this is set to 9600. | ||
| Parity | This can be set to one of the following: * None * Odd * Even |
||
| Stop Bits | This value can be either 1 or 2. | ||
| Data Bits | Enter a value between 5-9. | ||
| Advanced Settings | |||
| Zero on Failed Poll | The value if there is no response from the asset. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Use Batch Polling | To request batch responses from the asset. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Contiguous Batch Request Only | To request contiguous batch responses from the asset. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Use Multiple Write Commands | Do not change the default value. | ||
| Timeout | The time set to receive the data before it is reset. You can modify or keep the default value of 500. | ||
| Retries | The number of times the server requests for retransmission of data. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Max Read Bit Count | The maximum number of bits that the server reads in one read request. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Max Read Register Count | The maximum number of registers that the server reads in one read request. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Max Write Register Count | The maximum number of registers that the server writes in one write request. This is a non-editable field. | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset. You can view and edit the Data Model using the EI interactive mode, or by uploading a JSON file. Select one of the following:
|
Serial asset type settings
Errors can easily occur when configuring a serial port. For example:
- The wiring must be accurate. For example, see the hardware documentation for a Cisco IR829.
- The serial relay service should be configured correctly for the Guest OS. For example, see the Cisco IR1101 documentation and Cisco IR1800 documentation.
- The physical serial port must be correctly exposed to IoX via LocalManager.
To troubleshoot a serial interface:
- Make sure serial port is configured in propagate mode on the IOS level.
- A current workaround is to use just the 0x prefix as StartCode to specify an empty StartCode.
- For testing interface options only:
- Use a data model with a fixed message size of 1 byte and no start code.
- Verify that there is some data that is coming in to ensure that the connection is working.
- Once this is done, actual data model can be defined.
Serial Connector data model
A serial connector asset type has a reduced data type. For example:
The following combinations are allowed:
- One read attribute
- One read plus one write attribute
- One read/write attribute
Read attribute allows these config combinations:
- Message Size and Timeout
- StartCode and Message Size and an optional Timeout
- StartCode and EndCode and an optional Timeout
Start-/End-Code prefix handling:
- Prefix 0x allows to specify hex encoded binary data (e.g. 0x1310 -> CR+LF)
- Prefix ' allows to specify 'as-is'
Serial data model example:
{
"apiVersion": 1,
"connectionType": "SERIAL",
"fields": {
"data_string1": {
"label": "My Data String",
"datatype": "String",
"description": "serial read attribute",
"access": "READ"
"startCode": "$",
"endCode": "0x0a",
"messageSize":""
}
}
}
In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following additional fields.
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Details | |||
| Serial Port | Enter the port number. For example, /dev/ttyS0 | ||
| Serial Port Characteristics | |||
| Baud Rate | Search or add a value for the Baud Rate. By default, this is set to 9600. | ||
| Parity | This can be set to one of the following: * None * Odd * Even |
||
| Stop Bits | This value can be either 1 or 2. | ||
| Data Bits | This value can be either 7 or 8. | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset. You can view and edit the Data Model using the EI interactive mode, or by uploading a JSON file. Select one of the following:
|
NTCIP1202, NTCIP1203, NTCIP1204 asset type settings
EI supports three NTCIP devices. Use the Asset Type for the correct connection type.
- NTCIP 1202—Actuate Signal Controller
- NTCIP 1203—Dynamic Message Sign
- NTCIP 1204—Road Weather Information System
The basic configuration for all these three asset types include the host, port, and SNMP version.
Advanced settings like community or authentication data must be set depending on the SNMP version.
Each NTCIP asset type supports a set of static attributes in addition to the regular configurable attributes.
NTCIP 1202 – Configuration
- NTCIP1202 has an additional configuration to enable streaming and choose an ASC manufacturer or standard.
- Streaming protocol SAE J2735 Standard is activated by default.
- Disabling streaming falls back to OID polling for the SPaT data.
NTCIP 1202 – Data Model
- The NTCIP 1202 data supports the static attribute rawSPAT combining all signal phase and timing data of all phases into one JSON string message.
- Static attributes have to be selected as any other attribute.
- Currently, only SAE J2735 Standard is implemented as streaming protocol. Other streaming protocols will be rejected by the gateway.
- Additional attributes can be configured using any OID that the actual device supports.
- Configurable attributes can be set to either Read, Write, or Read & Write.
- Read & Write and Write attributes can write back data into the device.
NTCIP 1202 allows the streaming of data using standard and Asset manufactured protocols. The different protocols are:
Standard protocol
- SAE J2735 Standard: The J2735 Standard defines a message set, including data frames and data elements, designed for applications utilizing the 5.9 GHz Dedicated Short Range Communications for Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (DSRC/WAVE) communication systems.
- J2735-2020: The current integrated stack version of J2735 in the EI app is 2020, ensuring backward compatibility with 2016 messages.

- SAE J2735 Standard: The J2735 Standard defines a message set, including data frames and data elements, designed for applications utilizing the 5.9 GHz Dedicated Short Range Communications for Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (DSRC/WAVE) communication systems.
Asset manufactured protocols
- Trafficware
- Intelite
- Econolite
- Trafficware
SNMP Connector Utilizing NTCIP1202
SNMP connector is developed using NTCIP1202 connector. You can enable SNMP trap functionality for NTCIP 1202 assets by following these simple steps:
- Choose the NTCIP 1202 asset
- Provide the trap port information
- Select the preferred SNMP version (1, 2c, or 3)
Examples:
- Trap Data Model Configuration:
"Trap1": {
"category": "TELEMETRY",
"datatype": "String",
"description": "This is trap attribute",
"label": "TrapDefinition",
"oid": "1.3.6.1.4.1.47889.17.96",
"oidDataType": "INTEGER",
"service": "trap_receive"
}
- Combined Data Model:
{
"apiVersion": 1,
"connectionType": "NTCIP1202",
"fields": {
"Attribute1": {
"access": "Read",
"category": "STATIC_TELEMETRY",
"datatype": "String",
"description": "Testing Attribute Definition",
"label": "DefaultAttribute",
"oid": "rawSpat",
"pollingInterval": 300
},
"Custom1": {
"category": "ATTRIBUTE",
"datatype": "String",
"description": "This is optional customer attibute",
"label": "custom Attribute",
"required": false
},
"Trap1": {
"category": "TELEMETRY",
"datatype": "String",
"description": "This is trap attribute",
"label": "TrapDefinition",
"oid": "1.3.6.1.4.1.47889.17.96",
"oidDataType": "INTEGER",
"service": "trap_receive"
}
}
}
In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following fields:
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Asset Type Details | |||
| Type Name | Add asset type name | ||
| Connection Type | Add Connection Type in the field. Important: Select the NTCIP1202 connector as a Connection Type. |
||
| Configuration Details | |||
| IP Address or Host Name | Provide the IP address or Host Name. | ||
| SNMP Version | Provide SNMP Version. | ||
| Port | Provide NTCIP connector port number. Note: NTCIP1202 port number should never match Trap port number, and vice versa. |
||
| Trap Port | Provide Trap port number. Note: Trap port number should never match NTCIP1202 port number, and vice versa. |
||
| Enable Streaming | |||
| Intersection ID | Intersection ID is optional and depends on the user's specific use case. Users can choose to configure this field if it is required for their particular scenario. For example, in traffic use cases, this information is mandatory. |
||
| Intersection Name | Intersection Name is optional and depends on the user's specific use case. Users can choose to configure this field if it is required for their particular scenario. | ||
| Advanced Settings | The specific Advanced Setting details vary based on the SNMP Version. Provide the appropriate authentication information accordingly. | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset. You can view and edit the Data Model using the EI interactive mode, or by uploading a JSON file. Select one of the following::
|
Note: If NTCIP 1202 connector is configured with Trap definition then its mandatory to add trap port in Configuration Details.
Trafficware and Econolite binary streaming to SAE J2735 SPAT
The NTCIP 1202 specifies the logical interface between an Actuated Signal Controller (ASC) and the host systems that control them. The NTCIP 1202 is based on the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). To retrieve the Signal Phase and Timing (SPAT), it takes hundreds of requests which load ACS to process them. To reduce the number of requests, Trafficware and Econolight manufacturers provide proprietary binary streams. These are processed by the DS-Link more efficiently and reduce the load on ACS. SPAT information increases vehicle safety on the road. Cars receive SPAT information in a specific J2735 format which is transmitted over Dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) protocol.
To support J2735, a conversion was developed between SPAT which is retrieved from ACS in proprietary binary format to J2735 SPAT. Intersection ID is added which identifies ACS and it is a mandatory field for J2335 SPAT.
J2735 SRM/SSM to NTCIP 1211
The NTCIP 1211 standard is used in DS-Link to provide Transit Signal Priority (TSP) and Signal Control and Prioritization (SCP). SCP provides preferential treatment for certain vehicles (emergency, public transport, and so on) and improves traffic performance and throughput, including public transport. Some vehicles send a Signal Request Message (SRM) to apply for preferential treatment. SRM converts to NTCIP 1211 format, which allows changing the configuration of the ACS through SNMP requests. The DS-Link evaluates the request and sends a Service Status Message (SSM) to the message generator, either by granting or denying the request. The receiving RSU accepts a request for preferential treatment if the sender is authorized to issue such a request. This is handled by the IEEE 1609.2 Standard for Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE) using certificates. The authorized vehicles are equipped with these certificates to authorize the TSP requests.
Exploring NTCIP1202 Connector's Various Use Cases
The NTCIP 1202 connector has few use cases, and combination of different use cases is consolidated in the below table:
| Use Case | RawSpat | Intersection | Streaming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traffic Controller - J2735 Stream | Yes - User must input | Optional | Enabled |
| Traffic Controller - Binary Proprietary Stream | Yes - User must input | Required | Enabled |
| Traffic Controller - Polling RawSpat (maybe SRM) | Yes - User must input | Required | Enabled |
| Simple SNMP - Polling OID | No | Optional | Disabled |
| Simple SNMP - Polling OID & Trap | No | Optional | Disabled |
| Simple SNMP - Trap | No | Optional | Disabled |
NTCIP 1203 – Data Model
- The NTCIP 1203 data model has the static attribute displayedMessage which can be set to display a message on the DMS.
- Static attributes have to be selected as any other attribute.
- The attribute can also be read out for the current set message.
- Like NTCIP 1202, additional attributes can be configured using any OID.
NTCIP 1204 – Data Model
- The NTCIP 1204 data model has 6 static read-only attributes. Static attributes have to be selected as any other attribute. Like NTCIP 1202, additional attributes can be configured using any OID.
- location
- elevation
- temperature
- humidityAndPrecipitation
- visibility
- airQuality
RSU asset type settings
RSU4.1 – Data Model
The RSU asset type supports a set of static attributes in addition to the regular configurable attributes. Static attributes are always available and do not have to be configured.
- The static attributes, have a JSON string content and reflect incoming DSRC messages, except storeAndRepeatMessage and broadcastImmediately static attributes.
- The storeAndRepeatMessage must be set as an array of message objects. All previous messages will be overwritten by the new array.
- The current array of messages can be obtained by reading the attribute.
- The basic configuration for this asset type includes the host, port, and SNMP version.
- Advanced settings like community or authentication data must be set depending on the SNMP version.
RSU data model example:
{
"apiVersion":1,
"connectionType":"RSU",
"fields":{
"MyDataString":{
"label":"My Data String",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Rsu read attribute",
"oid":"1.0.15628.4.1.8.1.0",
"oidDataType":"INTEGER",
"pollingInterval":12345,
"category":"TELEMETRY",
"access":"Read"
},
"basicSafetyMessage":{
"label":"basicSafetyMessage",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Basic Safety Message",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"mapData":{
"label":"mapData",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Message to Display",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"spat":{
"label":"spat",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Signal Phase and Timing Message",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"commonSafetyRequest":{
"label":"commonSafetyRequest",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Common Safety Request",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"emergencyVehicleAlert":{
"label":"emergencyVehicleAlert",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Emergency Vehicle Alert",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"intersectionCollision":{
"label":"intersectionCollision",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"intersection Collision",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"nemaCorrections":{
"label":"nemaCorrections",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"NMEA Corrections",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"probeDataManagement":{
"label":"probeDataManagement",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Probe Data Management",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"roadsideAlert":{
"label":"roadsideAlert",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Roadside Alert",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"rtcmCorrections":{
"label":"rtcmCorrections",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"RTMC Corrections",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"signalRequestMessage":{
"label":"signalRequestMessage",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Signal Request Message",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"signalStatusMessage":{
"label":"signalStatusMessage",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Signal Status Message",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"travelerInformation":{
"label":"travelerInformation",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Traveler Information",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"personalSafetyMessage":{
"label":"personalSafetyMessage",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Personal Safety Message",
"access":"Read",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"broadcastImmediately":{
"label":"broadcastImmediately",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Instruct RSU to send a message",
"access":"Write",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
},
"storeAndRepeatMessage":{
"label":"storeAndRepeatMessage",
"datatype":"String",
"description":"Store & periodically broadcast messags",
"access":"ReadWrite",
"category":"STATIC_TELEMETRY"
}
}
}
In the Add Asset Type page, complete the following additional fields.
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Details | |||
| IP Address or Host Name | Enter the IP address or hostname. | ||
| Port | Enter the port number. | ||
| SNMP Version | Select a version from the drop-down list. 3 is the most secure version. | ||
| Advanced Settings | Complete the fields based on the selected SNMP Version. | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset. You can view and edit the Data Model using the EI interactive mode, or by uploading a JSON file. Select one of the following:
|
EIP/CIP asset type settings
In this release:
- Currently, only Explicit Messages (EM Tags) are supported.
- The basic configuration contains the host, port, and slot number of the PLC to connect to.
- Additionally, the message polling interval can be set.
- Rockwell CompactLogix PLCs have been tested to work.
Data Model:
- Each EIP/CIP asset type supports a set of configurable Explicit Message attributes.
- Additionally, custom attributes can be set.
- Cyclic IO Messages are currently not supported.
- The Data Type field is currently not used, and the result data type is defined by the sending PLC.
- Configurable attributes can be set to either Read, Write, or Read & Write.
- Read & Write and Write attributes allow to write back data into the device itself.
EIP/CIP data model example:
{
"apiVersion":1,
"connectionType":"EIPCIP",
"fields":{
"new_attribute":{
"label":"New Attribute",
"description":",
"datatype":"String",
"tagName":"test",
"tagType":"numeric",
"category":"TELEMETRY",
"access":"Read"
}
}
}
In the Add Asset Type page, refer to the following screenshot and complete the following additional fields:
| Field | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Details | |||
| IP Address or Host Name | Enter the IP address or hostname from where the data should be fetched. | ||
| TCP Port | The port of the PLC | ||
| Slot Number | The PLC slot to use | ||
| Explicit Message Polling Interval | The interval in ms to poll data | ||
| Data Model | Data Model explains how data is represented in the Asset. Use the EI interactive mode or upload a JSON file to view and edit the Data Model. Choose from the following:
|
EM Tag for EIP/CIP Asset Type
Tags are a method for assigning and referencing memory locations in PLC controllers (such as Allen Bradley Logix5000). EI supports the two different data formats that are used to create the EM tag. Find below:
- Atomic Data type (single-level not having hierarchy)
- Composite Data type (Hierarchical or Sub Tag)
EM tag with Single Level
In EI, Atomic Data type is used in the data model as shown below:

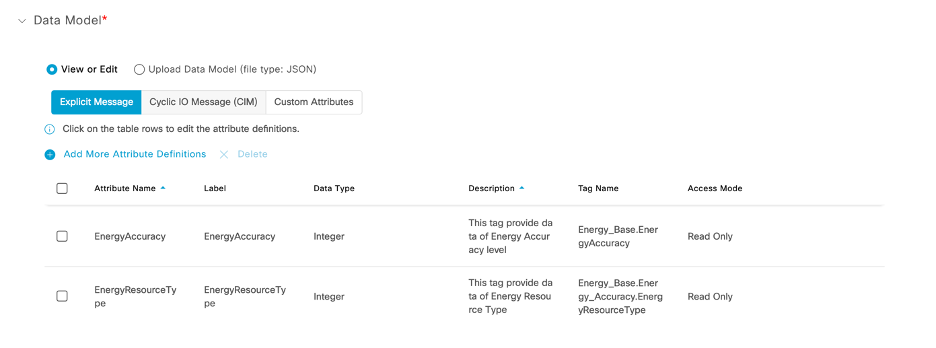
In this example, the Atomic EM Tag is EnergyResourceType, whose type is Integer.
EM tag with Multi-Level
The Hierarchical Data type for Energy_Base is:
Energy_Base
Energy_Resource
EnergyResourceType INT
BaseEnergyObjectCapabilities INT
EnergyAccuracy INT
Data Status INT
Note: The Composite Data type (Hierarchical Data Type/Sub Tag) can have multiple levels.
You can access Composite Data type using dot (.) operator in data model while creating the asset type.
For example:
Energy_Base.Energy_Resource.EnergyResourceType
Save & Verify Data Model
You can verify your data model before saving it.
- Physically Connect
- Get ready with your test network device & asset instance of the same asset type that is being verified.
- Ensure that the test network device & asset are physically connected.
- Select EI Agent on the chosen network device — Choose an EI Agent from the drop-down list. If you are unable to find the required EI Agent, click Ensure EI Agent is installed on your network device to check.