Network
Alert: Cisco has made the end-of-life (EOL) announcement for the Cisco Edge Device Manager (EDM).
Note: The IR800, IR1101, and IR1800 series devices provide similar Network functionality for QoS, Network QoS Rules, and Port Forwarding rules. IR1800 routers also provides a section for Static Route configuration for local routes.
Configuring the Network section enables you to choose the way in which network traffic is routed between nodes (devices). It enables you to configure what interfaces and what type of traffic is routed to those interfaces (IP Addresses). The IR1800 allows you to define up to eight port forwarding rules and six static routes.
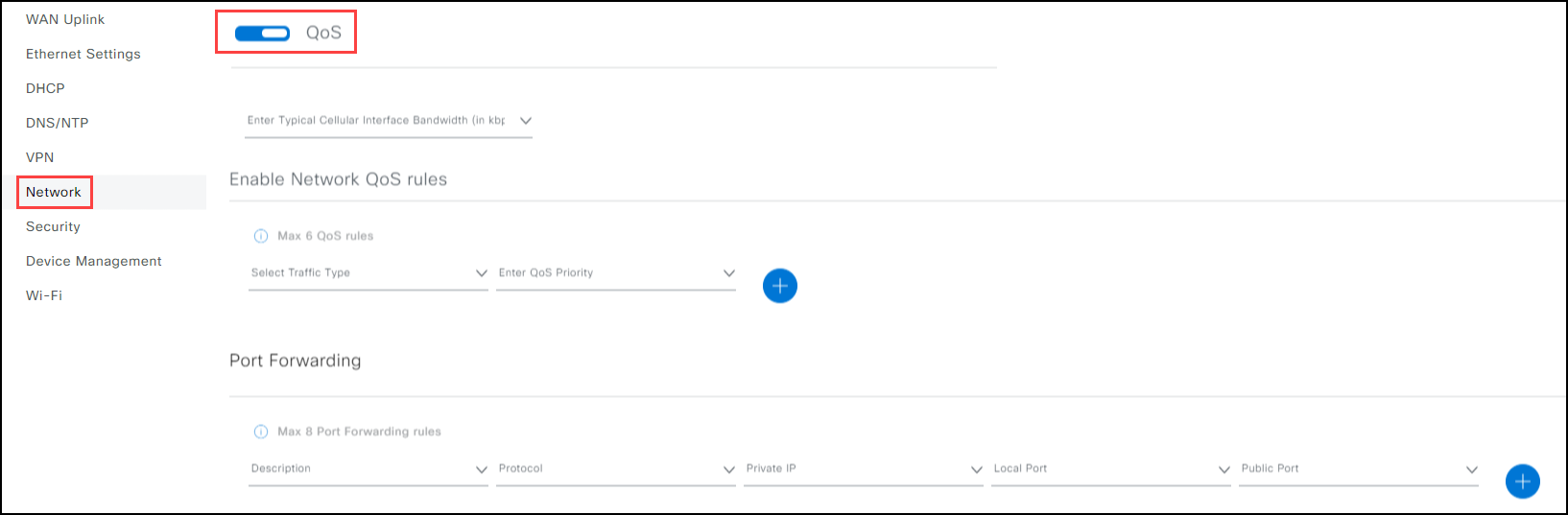
Quality of Service (QoS) and Network QoS Rules
QoS Traffic Types
The QoS function is disabled by default. That means that all types of network traffic between applications are treated the same. Enabling the QoS function allows the IR1800 device to prioritize network traffic to fit your needs. When you enable QoS you can select the optimum bandwidth that suites the type of traffic in your network and the size (how many devices) of the network for a data packet to reach the destination network.
Following is a list of traffic types:
- Broadcast TV (such as Live events, Video surveillance)
- Non-interactive data applications
- Multimedia Collaboration applications
- Video-On-Demand (VoD) streaming video
- Network control Plane traffic
- Network operations (such as Administration and management (customer) traffic)
- High-Definition (HD) interactive video applications
- Signaling traffic that supports IP voice and video telephony
- Interactive data applications
- Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) telephony traffic
Port Forwarding Rules
Port forwarding rules check the header of each inbound data packet and either block or forward each packet to the specified devices on your local network. For the eCVD IR1800, you can create up to eight rules. Each rule consists of the following:
- Description: A short phrase to describe the rule.
- Protocol: TCP preferred for targeting application-specific data for more reliability for video streaming or UDP preferred for video playback or DNS lookups and better for speed and efficiency, for example media streaming, VoIP, and online gaming.
- Private IP: A specific IP address for a port.
- Local Port: A specific port number (for example, 80 for HTTP) associated with an IP address within the local network. The range is 1-65535.
- Public Port: A public port number associated with an IP address that is outside the local network. The range is 1-65535.
Note: The public port is the port seen from the WAN side. The private port is the port being used to reach the destination network (they are usually the same).
Static Routes
Static routes provide fixed routing paths for a data packet to reach the destination network. They are manually configured on the device. Static routes are local to the device unless they are redistributed by a routing protocol. The IR1800 allows the creation of up to six static routes. It uses the following parameters:
- Destination Network: A specific network destination IP address.
- Destination Network Netmask: A set IP address that starts with 225 (for example 255.255.0.0 for 32-bit and 255.255.255.0 for 24-bit networks) to identify the network ID portion of the IP address.
- Destination Interface: The interface used. For example: Cellular 1 or Cellular 2 for modems, ethernet, VPN or Wi-Fi Uplink for SIM cards.
To configure your network:
- (Optional) If you need to control your devices, then Enable QoS (Quality of Service).
Note: If the QoS is Disabled, go to Step 3, Port Forwarding and Step 4, Static Routes.)
When QoS is enabled, set up the Network QoS:
a. (Required) Select the Traffic Type (per device).
b. (Required) Select the QoS Priority per device (High, Medium, or Low).
c. (Optional) Click
 to add more network QoS rules.
to add more network QoS rules.When QoS is enabled, configure the Port Forwarding:
a. Enter a Description of the device.
b. Select a Protocol (UDP or TCP).
c. Enter a Private IP Address.
d. Select a Local Port (range: 1-65535).
e. Select a Public Port (range: 1-65535).
f. (Optional) Click
 to add more port forwarding rules.
to add more port forwarding rules. Note: A maximum of six rules can be created.
(Required) Configure the Static Routes:
a. Enter the IP Address of the Destination Network.
b. Enter the Destination Network Netmask.
c. Select the Destination Interface.
d. (Optional) Click
 to add more static routes.
to add more static routes. Note: A maximum of eight routes is created.
Click Save. A success notice opens in the bottom right.
Network screen: QoS enabled