Overview
This module provides an in depth look at Cisco's industrial routing portfolio which is central to the RaMA (Remote and Mobile Assets) solution. This module can be used to help guide the design and implementation of the RaMA solution. Feature comparisons between the available models (for mobile and fixed applications) are presented, as well as recommendations for hardware use in several common use cases. Some troubleshooting tips are provided, along with issues to look out for when designing and deploying the industrial routers in the Remote and Mobile Assets solution. Finally, a hardware software matrix outlines all the versions validated as part of the solution Cisco Validated Design.
Requirements
- Portfolio of secure industrial gateways
- Secure cloud-hosted gateway deployment and management
- Zero-Touch Deployment (ZTD) and Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP)
- WAN connectivity options (Ethernet, LTE, Dual-LTE, WGB, and DSL)
- Wi-Fi hotspot
- GPS
- Enterprise network integration
- Security
- Lower deployment and operating expenses
- Higher asset uptime
- Edge compute
Figure 1: Cisco Remote and Mobile Assets—Solution Architecture—Component View
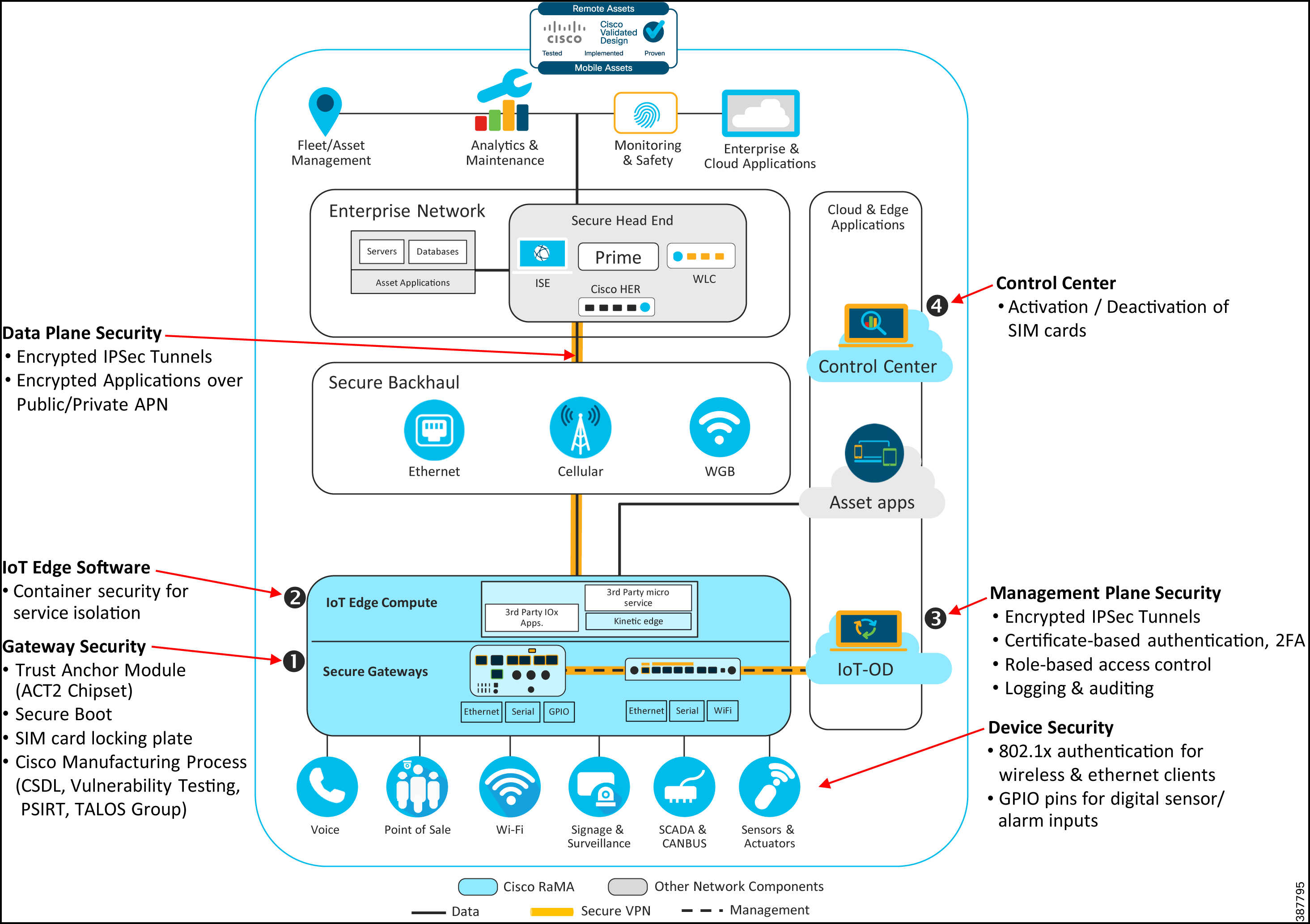
Figure 1 highlights the following four, primary components of the Cisco RaMA solution, the portfolio of Cisco Industrial Routers (IRs) and Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard:
- The Cisco IR portfolio consists of different models of hardened industrial grade gateways that can be installed with fixed and mobile assets. For mobile assets, the gateways can provide non-stop vehicle connectivity and an in-built GPS to track the current and historical location of the mobile asset.
- Cisco IOx provides the edge compute capability on supported IR gateways. The ability to run microservices (from Cisco or third parties) enables data collection, processing, and forwarding at the edge of the network.
- Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard is a cloud-hosted provisioning and management platform that enables ZTD and management of the edge routers. IoT Operations Dashboard establishes a secure IPSec management tunnel to each of the on-boarded routers for provisioning and managing the routers from a centralized cloud. If customers wish to extend their enterprise network to the edge IoT gateways, IoT Operations Dashboard helps provision a FlexVPN tunnel from each of the edge gateways to the enterprise headend VPN router.
- Cisco Control Center works with supported cellular providers to enable customers to manage the SIM cards and associated data plans for IoT devices. Integration with IoT Operations Dashboard streamlines the management of cellular-connected Cisco gateways.
Design Considerations
Getting started with the Cisco RaMA solution requires two steps:
- Selecting the industrial router model
- Designing the solution
Selecting the Router
Figure 2: Cisco IoT Gateway Portfolio
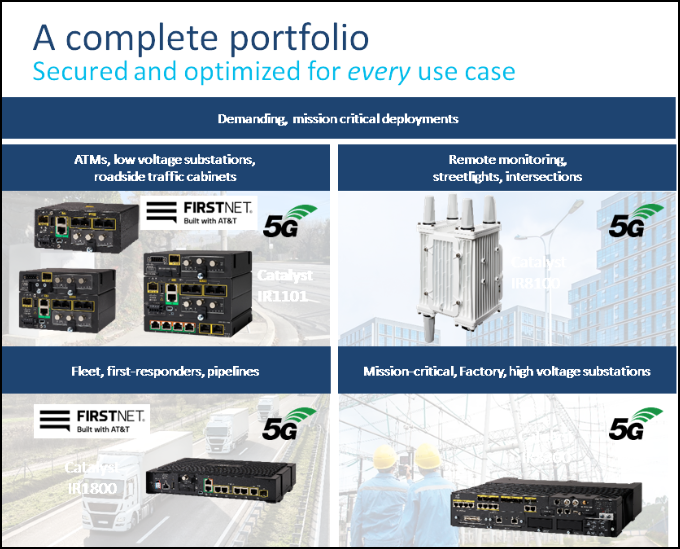
Cisco offers a wide range of industrial routers to meet a range of requirements and budgets. Table 1 lists some of the prominent features supported by each of the routers.
Table 1: Industrial Router Options
| Router | Catalyst IR1101 Rugged1 | Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Series2 |
|---|---|---|
| Features | Highly modular design: * Din rail mounting * Wall mounting * Panel mounting * Modular LTE and 5G ready * SCADA integration * Utility certifications * SDWAN ready * Powered by Cisco IOS XE |
Modular design with mobile features: * Din rail mounting * Wall mounting * Panel mounting * Ignition power management * Modular LTE and 5G ready * SCADA integration * Automotive certifications * SDWAN ready * Powered by Cisco IOS XE |
| Ports and Backhaul | Four Fast Ethernet * Single and Dual Cellular (Dual SIM) * One serial port (RS232 DTE) * WAN SFP port (GigabitEthernet or DSL) |
* Four RJ45 with switch ports (10/100/1000 Mbps) with PoE+ * Single and Dual Cellular (Dual SIM) * 1 or 2 serial ports (RS232 or RS232/RS485) * WAN SFP port |
| Expansion Modules | IRM-1100-SPMI * 2 SFP GE LAN Ports * Slot for pluggable module (typically a second cellular modem) * 4 GPIO ports IRM-1100-4A2T * -2 GE RJ45 LAN (L2) Ports * 4 Asynchronous Serial Ports (RS232/RS485) (DCE) |
|
| Wi-Fi and WGB | None | Optional 802.11ax Wi-Fi6 module 2.4GHz and 5GHz radio for Wi-Fi hot spot operation and WGB respectively |
| Embedded Sensors | GPS, Digital I/O (with IRM-1100-SPMI) | GPS, Digital I/O, Ignition sense, CANbus, Gyroscope, Accelerometer |
| Edge Compute | * 1255 CPU units for edge compute * 862MB memory * 701MB storage * mSATA storage module (65GB) |
Models IR1821, IR1831, IR1833: * 1617 CPU units for edge compute * 862MB memory * 512MB storage Model IR1835 has a greater CPU and memory availability. * Can add storing module for mSATA (65 GB) |
| Power Consumption | * 10w typical * 12w max |
* 22w typical * 71w max (with PoE) |
| Other Features | IP30, Fanless | IP40 (IP54 enclosure available), Fanless * Shock and vibration proof |
| Dimensions (inches) and Availability | 2.36 x 5.22 x 4.92 base unit (no expansion modules) in North America and Europe | 2.20 x 11.04 x 8.06 inches (globally) |
Designing the Solution
Target Customers and Markets
Target customers for the Cisco RaMA solution have similar application requirements for connecting their assets, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Application Requirements
| Typical Applications | Platform Requirements |
|---|---|
| Remote Assets | |
| Telemetry | SCADA-certified, ruggedized routers to meet stringent specifications |
| Asset Control | Edge compute options for automation and legacy protocols |
| Predictive Maintenance | Architecture for remote machine access and data acquisition |
| Mobile Assets | |
| Telematics | Best practices to deploy and manage at scale with a limited IT staff |
| Automatic Vehicle Location (AVL) | Integrated GPS and geofencing |
| Computer-Aided Dispatch (CAD) | Enterprise application integration using edge compute |
Despite these similarities, the target segments also have distinct requirements based on their industry. Typical users fall into six categories with a number of vertical industries covered by each, as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Target Customers and Markets
| Segment Category | Description | Sample Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Assets | ||
| Connected Machines | Enterprises with industrial equipment at distributed customer and indoor locations, including: * Conveyor belts, escalators, etc. * Indoor equipment |
* Real-time telemetry of machines at customer locations * Preventative maintenance/control without a truck roll * Flexible routing options based on available connectivity |
| Outdoor Equipment | Enterprises and public sector entities with industrial equipment in the field or at outdoor locations, including: * Oil and gas companies * Roadways and traffic management * Utilities |
* Ingress Protection (IP)-rated equipment to meet stringent temperature, dust, and operating specifications * Edge compute options for legacy protocols * SCADA-ready |
| Remote Sites | Connectivity for remote and distributed sites, including: * Retail and distribution centers * Kiosks * Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging |
* Remote setup and operations by field workers * Reliable data access and options for additional network services * Simplified cloud management |
| Mobile Assets | ||
| Service Fleets | Enterprises that use large fleets to deliver customer services as an extension of their business, including: * Utilities * Telco and cable * Specialized freight |
* Extend enterprise network to vehicles * Enterprise application integration using edge compute * Enterprise VPN termination and unified Wi-Fi policies |
| Buses and Taxis | Enterprises that use vehicles as their primary means of service delivery, including: * Bus companies * Taxi companies |
* Growing range of in-vehicle services (such as ticketing, Wi-Fi, video entertainment, and video cameras) * Vehicle telemetry, performance tracking, and driver safety * Deploy and manage at scale with limited IT staff |
| Public Safety Vehicles | Cities and municipalities that use fleets of specialized vehicles for citizen and municipal services, including: * Police vehicles * Ambulances * Fire trucks |
* Lives depend on an always-on connectivity * Frequent increase in vehicle devices (such as computers, dash cams, and sensors) * Multiple connectivity options (such as Single-LTE/Dual-LTE and Wi-Fi) |
Because of the flexibility of the Industrial Routers and the IoT Operations Dashboard software, the Cisco RaMA Cisco Validated Design describes several available options. Table 4 and Table 5 provide sample guidance for basic connectivity versus advanced connectivity to provide a flavor for the range of possibilities.
- The basic connectivity option provides basic internet connectivity for edge device(s) behind the IR, with a focus on easy deployment and minimal requirements from the enterprise network.
- The advanced connectivity option provides more complex architectures for experienced customers to use their edge gateways as a full extension of the enterprise.
All gateway configuration options shown throughout are implemented using Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard config templates. Table 4 and Table 5 are examples that demonstrate the range of design options available through IoT Operations Dashboard. Actual customer requirements should drive the technology decisions since those use cases may look different from the options shown below.
Although Cisco IOS provides many more options and features, these are outside the scope of this document. Mixing IoT Operations Dashboard and manual configuration is not recommended. For use cases that require advanced IOS configuration not exposed via Base IoT Operations Dashboard config templates, we recommend using the Advanced Templates feature within IoT Operations Dashboard.
Table 4: Remote Assets Use Cases
| Use Case | Advanced Connectivity |
|---|---|
| Hardware | IR1101 |
| WAN backhaul | Single cellular standard Optional 5G and FirstNet Optional dual cellular (with expansion module) Dual SIM Wired Gigabit Ethernet |
| Edge device connectivity | Wired Fast Ethernet Serial |
| Outbound connectivity from gateway | Private APN or Public APN + FlexVPN, access to enterprise (and internet) |
| Inbound connectivity to gateway and edge devices | FlexVPN site-to-site tunnel, or Secure Equipment Access |
| LAN addressing | Custom subnet, routed mode, and NAT |
| Edge device authentication | 802.1X |
| Compute onboard router | IOx with optional mSATA storage |
| General Purpose I/O for discrete signal status monitoring or control | IRM-1100-SPMI * 4 GPIO ports |
Note: The IR1800 Series router can also be used for remote assets use cases if Wi-Fi or other hardware specific features need to be used.
Table 5: Mobile Assets Use Cases
| Use Case | Advanced Connectivity |
|---|---|
| Hardware | IR1800 Series |
| WAN backhaul | Dual cellular Optional 5G and FirstNet Dual SIM Wired Gigabit Ethernet Wi-Fi WGB CURWB connectivity to IW9165 or IW9167 |
| Edge device connectivity technology | WiFi6 dual band (2.4GHz, 5GHz) Wired Gigabit Ethernet with PoE+ Serial CANbus |
| Outbound connectivity from network device | Private APN or Public APN + FlexVPN, access to enterprise (and internet) |
| Inbound connectivity to gateway and edge devices | FlexVPN site-to-site tunnel or Secure Equipment Access |
| LAN addressing | Custom subnet, routed mode, and VRF |
| Edge device authentication | Wireless-WPA2 with 802.1X |
| Compute onboard router | IOx with optional mSATA storage |
Note: The 1800 Series router can also be used for remote assets use cases if Wi-Fi or other hardware specific features need to be used.
Cisco Industrial Router Portfolio
This section describes the Cisco IR portfolio hardware and networking features. When evaluating specific hardware or software features in this section, the Industrial Router platforms that support the described feature are indicated.
Cisco IR1101 Rugged Routers
The Cisco Catalyst IR1101 Rugged Series (IR1101) is Cisco's smallest module industrial router. Built for flexible deployment options via additional expansion modules, it supports multi-path LTE and 5G as well as DSL WAN backhaul connectivity for mission-critical IoT initiatives requiring highly-secure data delivery, and redundant connectivity for fixed location applications. With two cellular modems, the IR1101 can concurrently connect to two cellular networks for high reliability or throughput, or to wired connections such as fiber or DSL. Additional modules can be added to expand connectivity to serially connected devices using various industry protocols as well as monitor and control connected devices using general purpose I/O.
Figure 3: Cisco Catalyst IR1101 Rugged Router (without expansion module)

Figure 4: Cisco IR1101 Expansion Module

Figure 5: Cisco IR1101 IRM-110-4A2T Expansion Module

- Cisco IR1101 Datasheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/1101-industrial-integrated-services-router/datasheet-c78-741709.html
- Cisco IR1101 Hardware Installation Guide: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/access/1101/b_IR1101HIG.html
Cisco Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Router
The Cisco Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Series (IR1800) is Cisco's most versatile IoT network device, purpose built for deployment on board a vehicle, but also widely used in fixed installations. The available modularity provides multi-path LTE and/or WAN backhaul for mission-critical IoT initiatives requiring highly-secure data delivery, edge application execution, and redundant connectivity. With two cellular modems, the IR1800 can concurrently connect to two cellular networks for high reliability, enhanced data throughputs, load balancing, and differentiated services. Additional modules can be added to expand connectivity with Wi-Fi6 and edge compute storage.
Figure 6: Cisco Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Network Devices

- Cisco IR1800 Datasheet: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/catalyst-ir1800-rugged-series-routers/nb-06-cat-ir1800-rugged-ser-rout-ds-cte-en.html
Select Hardware Features
Choice of Antennas
All Cisco hardware offer a wide range of antenna options to support the use case requirements. Best practices for antenna installation include:
- Antenna should offer MIMO on LTE. Without MIMO, WCDMA, UMTS, HSPA, and DC-HSPA+ are only possible for diversity. In the case of 3G UMTS, a solo antenna limits switching to the diversity port.
- Install the router with two antennas (Main and Aux) to guarantee the best performance level. A single antenna may affect downlink performance by more than 3dB and by as much as 20dB because of multipath fading (destructive interference between direct and reflected radio waves).
- We recommend the use of multi-element antennas (5-in-1, 3-in-1, 2-in-1) to avoid streams interfering with each other. If, instead, MIMO antennas that have a strong correlation coefficient were installed, the system may have trouble separating them (leading to interference).
- On the IR1800, ensure physical spacing between antennas to allow for RF isolation between different radios. The router requires a guaranteed >15dB (ideally 20-25dB) isolation between Wi-Fi and LTE antennas to ensure optimum performance.
For guidance on antenna installation for the different gateways (Cellular Antenna, WLAN Antenna-5 Ghz, WLAN Antenna- 2.4GHz), refer to the Cisco Industrial Routers and Industrial Wireless Access Points Antenna Guide at: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/connectedgrid/antennas/installing-combined/industrial-routers-and-industrial-wireless-antenna-guide.html
To help with antenna selection, refer to the Antenna Selection Table at: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/connectedgrid/antennas/installing-combined/industrial-routers-and-industrial-wireless-antenna-guide/Antenna-Selection.html
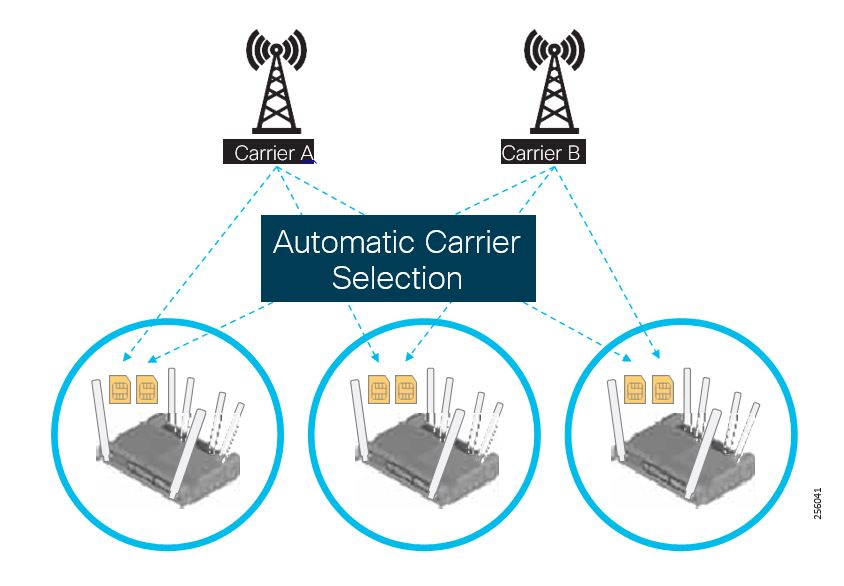
SIM-based Auto-Carrier Selection (AutoSIM)
The router automatically detects the active SIM and configures its modem for the appropriate cellular carrier when an active SIM is inserted and powered up, which provides several benefits including:
- Simplified configuration and reduced setup time
- Single SKU for all carriers
- Simplified procurement, reduced inventory complexity, and simplified deployments
Figure 7: Industrial Router Auto SIM
SSD Storage
The IR1101 and IR1800 (IR1833 and IR1835) Expansion module supports an optional mSATA Solid State Disk that is available in 100 GB capacity. This replaces the 4 GB of disk built-in storage available in the main unit and is only visible and usable in IOx. Once the module is installed, no additional configuration is needed to use the extra disk space. Since this module is not hot-swappable, the router will need to be powered off before installing the module.
General Purpose I/O (GPIO)
The IR1101 IRM-1100-SPMI expansion module has a connector for 4 GPIO signals. The Digital I/O supports Both Dry and Wet contacts up to 60 Volts.
- Dry contact is isolated from a voltage source (or “No Volt”), with an embedded relay function (NPN transistor), usually used to indicate an event. For example: open/close, alarm.
- Wet contact is a contact with external power (+3.3 V to +60 V, max 150 mA of current allowed at high voltage) applied, usually used to energize something. For example: solenoid, light.
For additional information on the GPIO pinouts, refer to Expansion Module product overview at: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/access/1101/b_IR1101HIG/b_IR1101HIG_chapter_01.html#con_1238158
Serial I/O
The IR1101 IRM-1100-42AT expansion module has four RJ45 connectors supporting additional serial ports. Each serial port can be configured for independent operation to support current and legacy devices using industry protocols, as well as UDP/TCP encapsulation and Reverse Telnet operations. For maximum serial ports, a second IRM1101-42AT can be attached on the alternate side of the IR1101.
For additional information on the Serial Ports, refer to Expansion Module product overview at: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/access/1101/b_IR1101HIG/b_IR1101HIG_chapter_01.html#con_1238158
Ignition Power Management
The Ignition Power Management feature helps keep the IR1800 network device up and running while the vehicle is stopped without draining the vehicle battery. Additional benefits of the Ignition Power Management system include:
- Zero boot up time (no cold start) because the platform stays powered up for a pre-determined period when the vehicle engine is turned off. The pre-determined period is programmable between 60 to 7200 seconds (2H00) using the IoS ignition off-timer command.
- Energy management by allowing users to program automatic power-down of the router when the vehicle battery drops below a certain voltage threshold.
- Automatic event logging including ignition state (on or off), ignition-off timer expiry, features enabled or disabled through the CLI, and under-voltage and over-voltage events.
- Ignition Sense feature on IR1835 can protect the router and vehicle battery by monitoring the input voltage on the main power connector.
Figure 8: Ignition Power Management Features

Figure 9: Ignition Power Management

Ordering Information
An updated list of supported hardware and firmware versions is maintained at: https://developer.cisco.com/docs/iotoc/#!supported-devices-and-firmware/supported-devices-and-firmware
To enable Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard on Cisco network devices, order the following option in the catalog:
- Option PID: IR-CLOUD-MGMT-Enable the network device to be ready for cloud management. Full ordering information is covered in the Ordering Guide: https://salesconnect.cisco.com/#/content-detail/72a7aefc-d93e-43a1-8584-fe964cb8b6a4
Once the base router is selected, options for specific hardware models and IoT Operations Dashboard subscription terms are made available. The available hardware SKUs supported in IoT Operations Dashboard are listed in the next section.
IoT Operations Dashboard Network Device Compatibility
IoT Operations Dashboard supports the management of Cisco IR1101 models as shown in Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, and Table 9.
| Router Part # | Description |
|---|---|
| IR1101-K9 | Cisco IR1101 Integrated Services Router Rugged with SL-IR1101-NE (Network Essentials) software license |
| IR1101-A-K9 | Cisco IR1101 Integrated Services Router Rugged with SL-IR1101-NA (Network Advantage) software license |
| Expansion Module Part # | |
| IRM-1100-SPMI | Expansion module for dual active LTE, 1 GE SFP and 1 Pluggable Module, 1 Digital GPIO Connector, and 1 mSATA SSD Slot |
| IRM-1100-SP | Expansion module for dual active LTE, 1 GE SFP and 1 Pluggable Module |
| IRM-1100-4A2T | Expansion module with 4 RJ45 serial ports and 2 Gigabit Ethernet (GE) ports |
| IR1100-SSD-100G | 100 GB mSATA SSD |
| Cellular Module Part # | |
| P-LTEA-EA(=) | Category 6 LTE module for North America, Europe and Middle East |
| P-LTEA-LA(=) | Category 6 LTE module for Asia Pacific and Latin America |
| P-LTE-MNA(=) | Category 4 LTE module for AT&T (FirstNet) and Verizon, US |
| P-LTE-US(=) | Category 4 LTE module for AT&T, U.S |
| P-LTE-VZ(=) | Category 4 LTE module for Verizon, U.S |
| P-LTE-GB(=) | Category 4 LTE module for Europe |
| P-LTEAP18-GL | Category 18 LTE module North America, Europe, Japan, Australia, and NZ |
| Power Supply Part # | |
| PWR-IE50W-AC-L= | AC power adapter for 110/220V AC and 88-300V DC input (temperature profile: -40C to 60C) |
| Router Part # | Description |
|---|---|
| IR1821-K9 | IR1800 Series Router with single pluggable slot |
| IR1831-K9 | IR1800 Series Router with dual pluggable slots |
| Cellular Module Part # | |
| P-LTEAP18-GL(=) | Category 18 LTE module for North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific |
| P-LTEA-EA(= | Category 6 LTE module for North America, Europe, and Middle East |
| P-LTEA-LA(=) | Category 6 LTE module for Asia Pacific and Latin America |
| P-LTE-MNA(=) | Category 4 LTE module for AT&T, FirstNet Ready and Verizon, US |
| P-LTE-US(=) | Category 4 LTE module for AT&T, U.S |
| P-LTE-VZ(=) | Category 4 LTE module for Verizon, U.S |
| P-LTE-GB(=) | Category 4 LTE module for Europe |
| P-LTE-IN(=) | Category 4 LTE module for India |
| P-LTE-JN(=) | Category 4 LTE module for Japan |
| Wi-Fi 6 Module Part # | |
| WP-WIFI6-x(=) | Module shipped in CAPWAP mode |
| WP-WIFI6-EWC-x(=) | Module shipped in EWC mode |
| SSD Part # | |
| IRM-SSD-100G(=) | A100-GB industrial-grade field-replaceable SSD |
| Power Supply Part # | |
| PWR-MF4-125W-AC(=) | AC to DC power adapter for IR1800- 125W |
| OBD-II Cable Part # | |
| OBD2-J1962YA-MF4(=) | OBD-II (J1962) Type A to IR1800 cable with type 1 Y-splitting bypass harness |
| OBD2-J1962YB-MF4(=) | OBD-II (J1962) Type B to IR1800 cable with type 2 Y-splitting bypass harness |
| OBD2-J1939Y2-MF4(=) | OBD-II (J1939) Type 2 heavy duty diagnostic harness for Volvo/Mack |
| OBD2-J1939Y1-MF4(=) | OBD-II (J1939) Type 1 to IR1800 cable with type 1 y-splitting bypass harness and auxiliary (discrete voltage) inputs |
| OBD2-J1708Y-MF4(=) | OBD-II (J1708) to IR1800 cable with type 1 y-splitting bypass harness and auxiliary (discrete voltage) inputs |
| OBD2-J1962VMB-MF4(=) | J1962-VM-Type B Volvo & Mack |
Table 8: IIR1101 and IR1800 Cellular Modules: Available LTE Advanced (3GPP Category 6) Modules
| Region | P-LTEA-EA | P-LTEA-LA |
|---|---|---|
| LTE Bands | LTE bands 1-5, 7, 8, 12, 13, 20, 25, 26, 29, 30, and 41 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 12), 700 MHz (band 29), 800 MHz (band 20), 850 MHz (band 5 CLR), 850 MHz (band 26 Low), 900 MHz (band 8), 1800 MHz (band 3), 1900 MHz (band 2), 1900 MHz (PCS band 25), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS), 2100 MHz (band 1), 2300 MHz (band 30), or 2600 MHz (band 7) TDD LTE 2500 MHz (band 41) Carrier aggregation band combinations 1+8; 2+(2,5,12,13,29); 3+(7,20); 4+(4,5,12,13,29); 7+(7,20); 12+30, 5+30, and 41+41 |
LTE bands 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 18, 19, 21, 28, 38, 39, 40, and 41 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 28), 850 MHz (band 5 CLR), 850 MHz (bands 18 and 19 Low), 900 MHz (band 8), 1500 MHz (band 21), 1800 MHz (band 3), 2100 MHz (band 1), or 2600 MHz (band 7) TDD LTE 1900 MHz (band 39), 2300 MHz (band 40), 2500 MHz (band 41), or 2600 MHz (band 38) Carrier aggregation band combinations: 1+(8,18,19,21); 3+(5,7,19,28); 7+(5,7,28); 19+21, 38+38, 39+39,40+40, and 41+41 |
| United States | Verizon, AT&T Mobile | |
| Canada | Yes | |
| Australia & New Zealand | Yes | |
| Japan | Yes | |
| India, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand | Yes | |
| UAE | Yes |
Table 9: IR1101 and IR1800 Cellular Modules: Available LTE (3GPP Category 4) Modules
| Region | P-LTE-VZ | P-LTEA-US | P-LTEA-GB | P-LTEA-MNA | P-LTEAP18-GL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTE Bands | LTE bands 4,13 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 13), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS) |
LTE bands 2, 4, 5, 12 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 17), 700 MHz (band 12), 850 MHz (band 5 CLR), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS) |
LTE bands 1, 3, 7, 8, 20, 28 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 28), 800 MHz (band 20), 900 MHz (band 8), 1800 MHz (band 3), 2100 MHz (band 1), and 2600 MHz (band 7 |
LTE bands 2, 4, 5, 12, 13, 14, 17, 66 FDD LTE 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 66 Ext AWS), 700 MHz (band 17, 14, 13,12), 850 MHz (band 5 CLR), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS), 1900 MHz (band 2) |
LTE bands 1-5, 7, 8, 12-14, 17, 18-20, 25, 26, 28-30, 32, 38-43, 46, 48, 66, and 71 FDD LTE 600 MHz (band 71), 700 MHz (bands 12, 13, 14, 17, 28, and 29), 800 MHz (band 20), 850 MHz (bands 5, 18, 19, and 26), 900 MHz (band 8), 1500 MHz (band 32), 1700 MHz (bands 4 and 66), 1800 MHz (band 3), 1900 MHz (bands 2 and 25), 2100 MHz (band 1), 2300 MHz (band 30), 2600 MHz (band 7) TDD LTE 1900 MHz (band 39), 2300 MHz (band 40), 2500 MHz (band 41), 2600 MHz (band 38), 3500 MHz (bands 42 and 48), 3700 MHz (band 43), 5200 MHz (band 46) |
| United States | Verizon | AT&T Mobile | Multicarrier (AT&T and Verizon) | Yes | |
| Europe | Yes | Yes | |||
| Band 14 | Yes | ||||
| FirstNet Certification | In Progress |
IoT Operations Dashboard Subscription Details
IoT Operations Dashboard is available as part of a Cisco platform subscription. Cloud-hosted IoT Operations Dashboard is sold based on the number of network devices under management. You can purchase a subscription for a 12, 36, or 60-month period. Since Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard is a cloud-hosted platform, you will automatically receive periodic updates to stay up-to-date with the latest version of the software. You can choose to prepay the subscription price for the entire term or on an annualized basis.
IoT Operations Dashboard Services and Support
Your IoT Operations Dashboard base software subscription entitles you to limited 12x5 phone/TAC support. The limited support includes access to trained TAC personnel via phone, web, and email. In addition, support includes the continuous monitoring of the Cloud Operations. You can also access online resources, including the knowledge base and tutorials. No additional products, licenses, or fees are required to access basic support services with the Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard subscription. Enhanced support is available for an additional fee.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
For additional detailed troubleshooting procedures, refer to: https://developer.cisco.com/docs/iotoc/#!troubleshooting-issues/troubleshooting-issues.
Common Network Device Issues
Stuck in Registering for more than 10 minutes.
This usually indicates that the network device is not able to contact Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard:
- For cellular network devices, ensure that a SIM card was inserted and has a valid data plan.
- If Ethernet-based network devices are used, verify that the required network ports are open and that no firewalls are blocking the network device from reaching the internet.
Stuck in the In Progress State for more than 10 minutes:
- Ensure that the network device did not go offline, and internet connectivity is still present.
- Check the Gateway Event Logs under the Network Device Details page to see if the gateway registered successfully and was configured.
- Verify that the WAN interface configuration is correct in the template used to claim the network device.
Network Device is in Failed State:
- Ensure that the network device did not go offline and internet connectivity is still present.
- Check that the network device model and model for the associated template are the same.
- Verify that the WAN interface configuration is correct in the template used to claim the network device.
GPS Troubleshooting
If the network device location is not being updated correctly on the map view:
- Wait for the update to occur. The network location is updated every 30 seconds.
- If GPS is not in enabled state, check if the gateway was claimed using a configuration that enabled GPS. This can be checked in the Network Device Event Logs. There will be an entry indicating the configuration that was applied to the gateway. Ensure that the proper configuration was applied.
- Ensure that the correct GPS antennas are attached to the network device.
- Delete and reclaim the network device with the correct configuration if required.
Login Troubleshooting
- Ensure that you or your user has a valid account in the portal.
- Click Forgot Password to reset a password.
Customer VPN Troubleshooting
If the gateway is not able to establish a tunnel with the HER:
- Verify that VPN is enabled on the Gateway Current Config page.
- If the VPN is not enabled, check if the device was claimed using a configuration that enabled the Customer VPN. This can be checked in the Gateway Event Logs. There will be an entry indicating the configuration that was applied to the gateway. Ensure that the proper configuration was applied.
- Verify that the details entered for the VPN configuration are correct.
- Verify that the configuration on your HER is correct and that it allows the gateways to establish tunnels with the provided configuration.
- Delete and reclaim the gateway with the correct configuration if required.
Note: A known issue exists where site-to-site VPN tunnels and the site-to-site VPN tunnel IP Address on the Network Device Details page can take up to 30 minutes to update after it is successfully enabled.
Appendix A—Firewall Ports for IoT Operations Dashboard to Gateway Communication
Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard requires specific TCP/UDP network ports and IP protocols to be opened on the network firewall to communicate with the network devices. For the recommended settings, refer to Network Ports and Protocols.
Appendix B—Hardware and Software Matrix
This is the current supported network devices and firmware.